Topics
The ability to track, analyze, and optimize performance is vital for any business. This section is structured to equip you with the necessary knowledge to track, measure, and scale your business. In this section, you will:
- Learn about key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales, profits, customer acquisition costs, and conversion rates. These metrics are pivotal in gauging your business progress and ensuring you’re on track to meet your goals.
- Understand the significance of tracking and analyzing data in driving your business growth. We’ll delve into various tools and techniques for data gathering and interpretation, enabling you to make data-driven decisions for your business.
- Discover growth strategies specific to the POD industry that can propel your business forward. Knowledge about scaling strategies is vital for long-term success.
By the end of this section, you’ll be able to identify trends, pinpoint areas of improvement, and make data-driven decisions to grow your business.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are specific, quantifiable metrics used to measure a business’s performance against its goals and objectives.
- Specific metrics: KPIs are quantifiable measurements or indicators that help businesses track their performance against specific goals and objectives. KPIs are a subset of analytics, representing the most critical metrics that reflect the overall health and progress of a business.
- Goal-oriented: KPIs are closely tied to a company’s strategic goals and objectives. They are designed to provide a clear understanding of whether a business is on track to achieve its targets or needs to make adjustments to its strategies and tactics.
- Easy to understand: Unlike complex analytics, KPIs are usually simple, allowing stakeholders at all levels of an organization to quickly grasp the current state of a business’s performance. Examples of common KPIs include revenue growth, customer acquisition cost, and employee productivity.
- Regular monitoring: KPIs are typically monitored and reported regularly, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly. This allows businesses to maintain a pulse on their performance and make timely data-driven decisions.
E-commerce KPIs to Focus On
Understanding the role of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for e-commerce success. By monitoring a tailored set of KPIs, businesses can evaluate their progress toward goals and make informed strategic plans. Let’s explore some essential e-commerce KPIs that can guide your business growth.
What are KPIs?
KPIs refer to quantifiable performance measurements over time for a specific goal. They make setting achievable targets and tracking progress easier. , and driving informed decision-making across an organization. By monitoring KPIs, you can:
- Set clear goals and objectives for teams and individuals, promoting accountability and focus.
- Track progress toward targets, making strategic adjustments easier.
- Identify trends, patterns, and areas of strength or weakness within the organization.
- Promote a data-driven culture, where decisions are based on objective performance metrics rather than intuition or personal biases.
- Benchmark performance against industry standards or competitors, providing valuable context and perspective.
Defining KPIs
When outlining your e-commerce KPIs, consider:
- A clear measurement for each KPI.
- A target aligned with your measurement and goal timeframe.
- A consistent data source for accurate measurements.
- A reporting frequency – weekly or monthly, ensuring monthly tracking at a minimum.
Ignore Vanity KPIs
Vanity KPIs may look impressive but don’t provide any actionable insights or contribute to your overall growth or success.
- Lack of actionable insights: Vanity KPIs often fail to provide useful information to help you make data-driven decisions. For example, a high number of social media followers may look good, but it doesn’t necessarily mean those followers are engaging with your content or becoming customers. Instead, focus on metrics like engagement rates or conversion rates that provide insights into your marketing strategy’s effectiveness.
- Misleading data: Vanity KPIs can sometimes paint an inaccurate picture of your business’s performance. For instance, a sudden spike in website traffic may seem like a positive sign, but if that traffic doesn’t result in more conversions, it might be due to irrelevant or low-quality sources. Relying on vanity KPIs may lead to misguided decisions based on an incorrect understanding of your business’s health.
- Resource allocation: Focusing on vanity KPIs can lead to the misallocation of resources, as you may be investing time and effort into strategies that don’t drive actual business results. Concentrating on meaningful metrics that directly impact your business’s growth, such as customer acquisition cost or customer lifetime value, can help you make better decisions on where to allocate resources for the greatest return on investment.
- Irrelevant to business goals: Vanity KPIs often don’t align with your organization’s overarching goals and objectives. By ignoring vanity KPIs and concentrating on metrics tied to your business goals, you can ensure that your marketing efforts are directed toward achieving tangible results that contribute to your company’s success.
- Short-term focus: Vanity KPIs often emphasize short-term gains over long-term growth. By prioritizing meaningful metrics that reflect the long-term health of your business, such as customer retention rate or recurring revenue, you can develop strategies that foster sustainable growth rather than chasing temporary wins.
Examples:
- Social Media Likes: While social media likes can boost brand visibility, they do not necessarily translate into sales or long-term customer engagement.
- Page Views: A high number of page views does not always mean that visitors are engaged with your content or that they will make a purchase.
- Email Open Rate: While email open rates can give you an idea of your email marketing effectiveness, it is more important to focus on click-through rates and conversion rates.
Focus your time and resources only on meaningful metrics to make informed decisions for your business.
Essential eCommerce Metrics
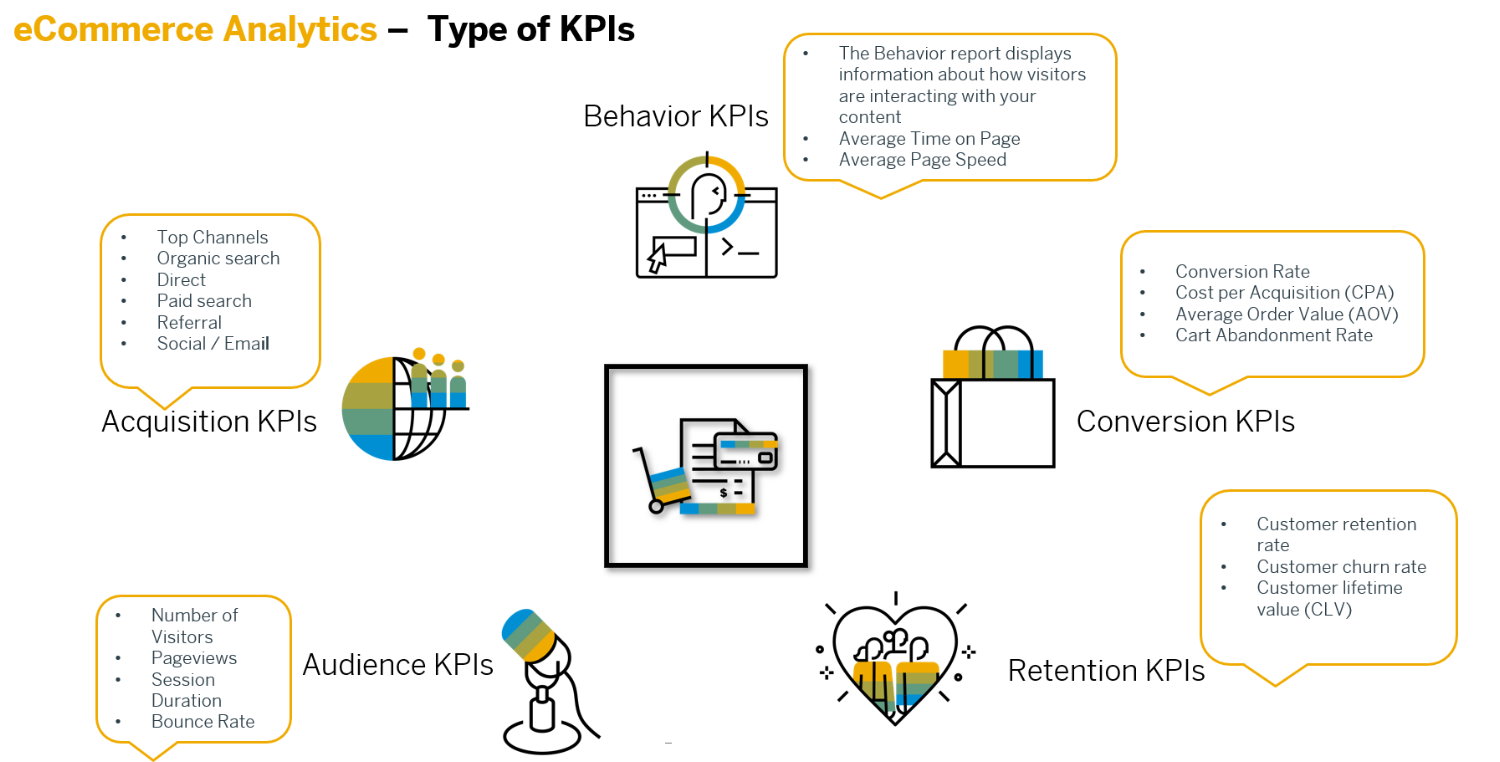
E-commerce businesses typically track a set of critical KPIs. Here are some crucial metrics:
- Sales Conversion Rate (SVR): SVR is s a metric that measures how effective your sales team is at converting leads into new customers. It’s calculated by dividing the total number of sales by the total number of qualified leads and multiplying by 100.
- Email KPIs: These metrics are used to track the effectiveness of an email campaign. Important email KPIs to consider are:
- Bounce rate: The percentage of emails that could not be delivered to subscribers.
- Conversion rate: The percentage of users who clicked on a link in the email and then completed a purchase or other desired action.
- Clickthrough rate: The number of people who opened the email and then clicked on a link.
- List growth rate: The rate at which a company’s email list expands.
- Open rate: The percentage of email recipients who open a given email.
- Sharing rate: The rate at which people share the email, which can improve your reputation and relationships with your audience.
- Return on investment (ROI): The overall revenue generated by the email campaign compared to the cost of managing the campaign.
- Deliverability rate: Similar to bounce rate, this metric indicates how deliverable the email is to the recipient’s inbox.
- Revenue per email: The total email revenue is divided by the total number of emails delivered.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV represents the total revenue or profit to expect from a customer over the course of the entire relationship with a customer. By understanding CLV, you have a better idea of what can be spent to acquire new customers and retain existing ones.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC measures how much is spent to acquire new customers. This typically includes all expenses that contribute to getting a sale.
- Revenue by Traffic Source: This metric breaks down revenue by marketing channel, highlighting the most valuable traffic sources such as social, organic search, paid search, or referral. The three main types of traffic sources are direct, referral, and organic. Direct traffic is when a visitor types your URL into the browser or finds you through an undefined source. Referral traffic is traffic from a link on another site.
- Average Order Value (AOV): AOV, considered one of the most important metrics, measures the average amount spent per order. It’s calculated by dividing total revenue by the number of orders that generated the revenue.
- Shopping Cart Abandonment Rate: This metric identifies what percentage of users signal purchase intention, but don’t complete the sale. It is calculated by dividing total revenue by the number of orders that generated the revenue.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty and satisfaction. This customer satisfaction benchmark measures how likely customers are to recommend a business to a friend. NPS is calculated by asking customers one question: “On a scale from 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product/company to a friend or colleague?”. The accumulated ratings are reported as a number between -100 and +100, with a higher score being desirable.
The importance of specific KPIs can vary based on factors like industry, leadership, and company culture. For instance, if your business heavily relies on social media, you might track specific social media KPIs like likes, followers, shares, comments, and profile visits.
Data Driven by Jeffalytics
Monthly KPI Tracking
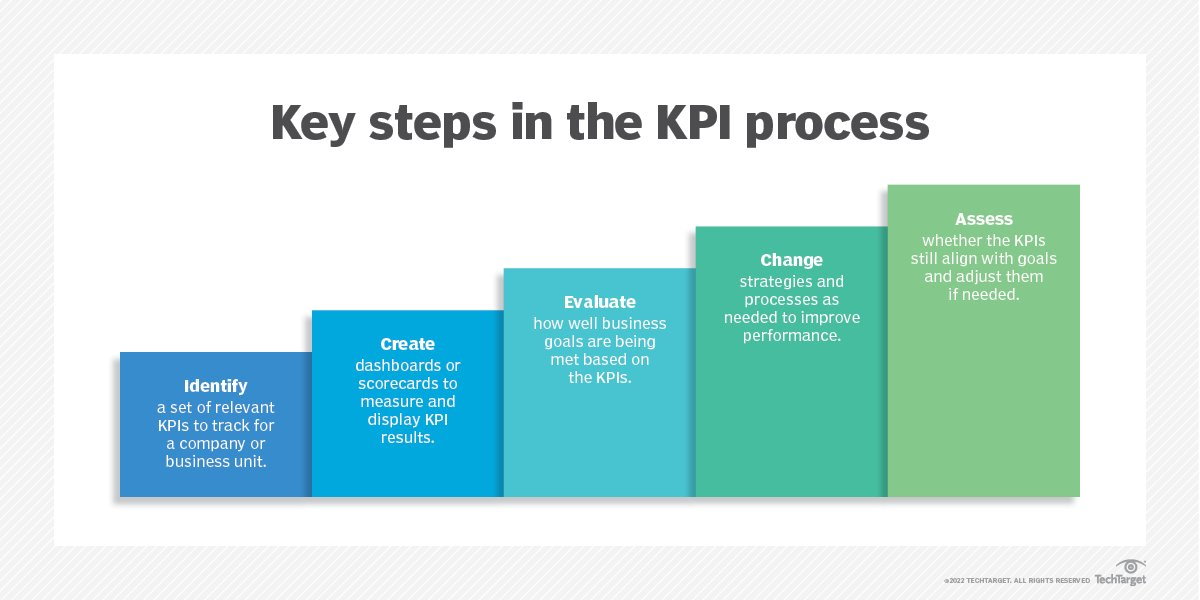
Monthly tracking of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) equips eCommerce marketing managers with a comprehensive understanding of their brand’s performance, trends, and potential improvement areas. Let’s examine some important eCommerce KPIs to monitor every month:
Cost Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC measures all the marketing and sales expenses incurred to convert a prospect into a paying customer. These expenses range from advertising to content creation, promotions, employee salaries, and other customer acquisition-related costs. CAC is calculated before sales taxes and includes adjustments for discounts, incentives, and other additional expenses.
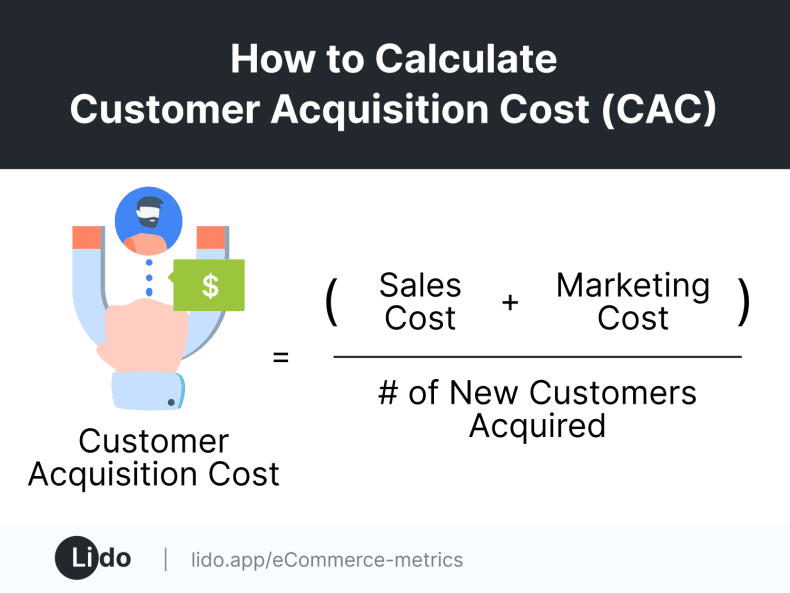
CAC Calculation:
1. Total marketing and sales expenses: This includes costs such as advertising, content creation, promotions, employee salaries, and any other expenses directly related to acquiring customers.
CAC = (Sales Cost + Marketing Cost) / Number of New Customer Acquired
2. Choose a time frame: Decide monthly, quarterly, or yearly based on your preference and business needs.
 For a deeper understanding of customer acquisition, formula calculation, and CAC knowledge that can benefit your business, check out this article Lido: Customer Acquisition Cost Formula.
For a deeper understanding of customer acquisition, formula calculation, and CAC knowledge that can benefit your business, check out this article Lido: Customer Acquisition Cost Formula.
Customer Lifetime Value (CTV)
CLV is an estimate of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a single customer. It helps businesses comprehend the long-term value of their customers and shape customer acquisition, retention, and marketing strategies accordingly. A customer is considered profitable if their CLV exceeds their acquisition cost.
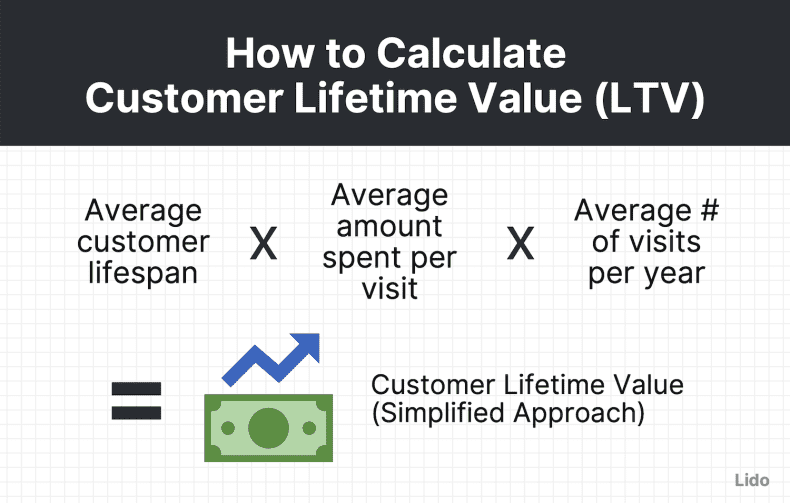
LV Calculations:
1. Calculate Average Purchase Value (APV): Divide total revenue generated during a specific period by the total number of purchases made during that same period.
APV = Total Revenue / Number of Purchases
2. Calculate Average Purchase Frequency Rate (APFR): Divide the total number of purchases made during a specific period by the total number of unique customers who made purchases during that same period.
APFR = Number of Purchases / Number of Unique Customers
3. Calculate Customer Value (CV): Multiply the Average Purchase Value by the Average Purchase Frequency Rate to calculate the customer value.
CV = APV x APFR
4. Calculate Average Customer Lifespan (ACL): Estimate the average duration (in years or months) a customer continues to make purchases from your business.
5. Determine Lifetime Value (LTV): Multiply the Customer Value by the Average Customer Lifespan to calculate the customer lifetime value.
LTV = CV x ACL
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV and LTV are often used interchangeably. LTV shows the amount that all customers will bring over the total time they interact with a company. CLV shows how much an individual customer will bring over the total time they interact with a company
 Knowing your Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) gives you an advantage in knowing how much to spend on acquiring customers. Without this information, you have zero facts to determine if your marketing methods are cost-effective. For a deeper understanding of CLV and how it relates to profit margins, customer retention, and more check out this article Lido: Customer Lifetime Value.
Knowing your Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) gives you an advantage in knowing how much to spend on acquiring customers. Without this information, you have zero facts to determine if your marketing methods are cost-effective. For a deeper understanding of CLV and how it relates to profit margins, customer retention, and more check out this article Lido: Customer Lifetime Value.
E-Commerce KPIs
- Average Delivery Time: Monitor the time it takes for products to be delivered to customers to ensure customer satisfaction and identify potential logistical issues.
- Time to Market: Measure the time it takes for products to reach the market and identify potential bottlenecks or lost sales opportunities.
- Employee Churn Rate: Track employee turnover to identify potential issues with company culture or employee satisfaction.
Sales KPIs
- Number of Engaged Qualified Leads in the Sales Funnel: Gauge potential growth opportunities by assessing the number of leads actively engaged in the sales process.
- Hours of Resources Spent on Sales Follow-Up: Analyze the time spent by your sales team following up on leads to optimize resource allocation.
- Average Time for Conversion: Measure the time it takes for leads to convert into sales, identifying potential barriers to conversion.
- Net Sales – Dollar or Percentage Growth: Track monthly sales growth to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing strategies and adapt as needed to achieve goals.
Other KPIs
- ROI on Marketing Spend: Measures profit percentage after accounting for marketing expenses.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS gauges customer loyalty and their likelihood of recommending your brand to others.
- Percentage of Returning Customers: Reveals the proportion of customers making repeat purchases, indicating customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Month-on-Month Sales Growth (MOM): Measures sales growth from one month to the next, highlighting the success of marketing and sales strategies.
- Traffic Source: Analyzes where your traffic originates, such as organic search, paid ads, or social media.
- Mobile Site Traffic: Tracks the number of users visiting your site from mobile devices.
- Email Subscriber Rate: Tracks the percentage of new subscribers to your email list.
- Average Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measures the percentage of users who click on a link within your content, such as an email, social media post, or ad.
Daily KPI Tracking
Monitoring daily KPIs is crucial for eCommerce businesses to gauge performance and quickly adapt to any changes. Here’s a closer look at the top eCommerce KPIs you should monitor daily:
eCommerce Conversion Rate (eCR)
eCR shows the percentage of visitors who make a purchase on your site. This metric helps you assess the potency of your marketing strategies, website design, and user experience.
Desktop users typically have an average conversion rate of around 3.83%, mobile users around 2.03%, and tablets match desktops at approximately 3.84%. These numbers can fluctuate based on your industry and target audience, but they provide a broad benchmark.
eCR Calculation:
eCR = (Number of Sales / Number of Visitors) x 100
Example: If your online store receives 10,000 visitors in a month and records 200 sales, your eCommerce conversion rate would be:
eCR = (200 / 10,000) x 100 = 2%
Regular tracking and analysis of your eCR let you spot areas for improvement, guiding data-driven decisions to boost your website’s performance, marketing campaigns, and revenue.
Cost per Click (CPC)
CPC is a standard advertising metric for online marketing campaigns. It’s based on your actual cost-per-click (actual CPC), which is the actual amount you’re charged for a click on your ad.
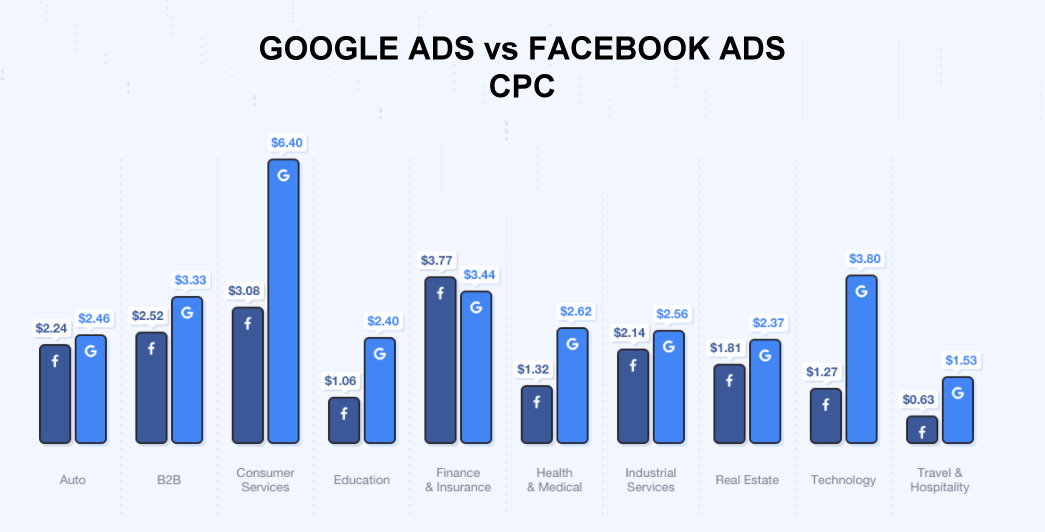
CPC Calculation:
Avg CPC = Total Cost of Clicks / Total Number of Clicks
Example: If an advertiser spends $500 on a campaign that generates 250 clicks, the average CPC would be calculated as:
Avg CPC = $500 / 250 = $2
Tracking of average CPC helps you assess the effectiveness of your ad campaigns, and optimize bidding strategies, targeting, and ad creatives, aiming for better results at lower costs. Monitoring CPC is key to maximizing ROI and effective ad spend distribution across marketing channels.
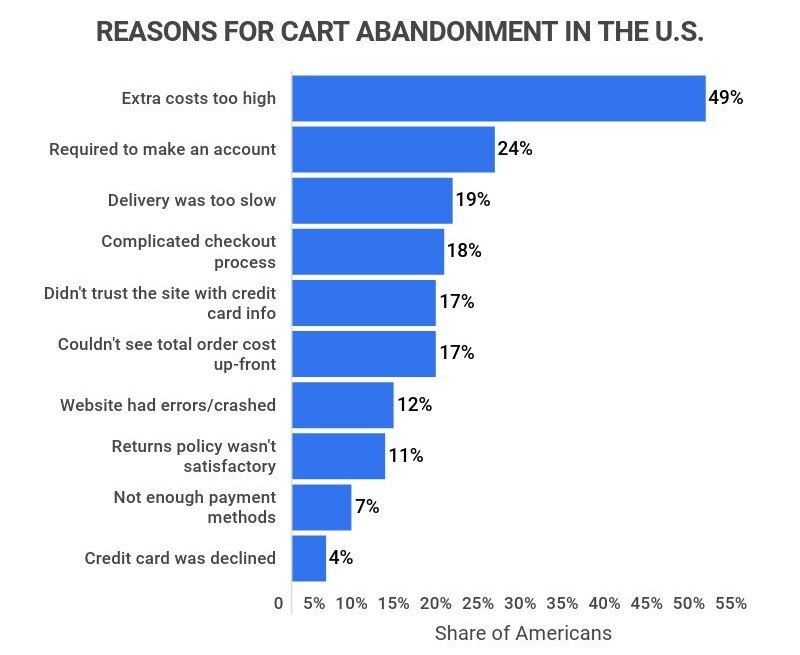
Cart Abandonment Rate (CAR)
CAR indicates the percentage of online shoppers who add items to their carts but do not complete the purchase. This rate highlights potential issues in the checkout process and helps optimize the user experience.
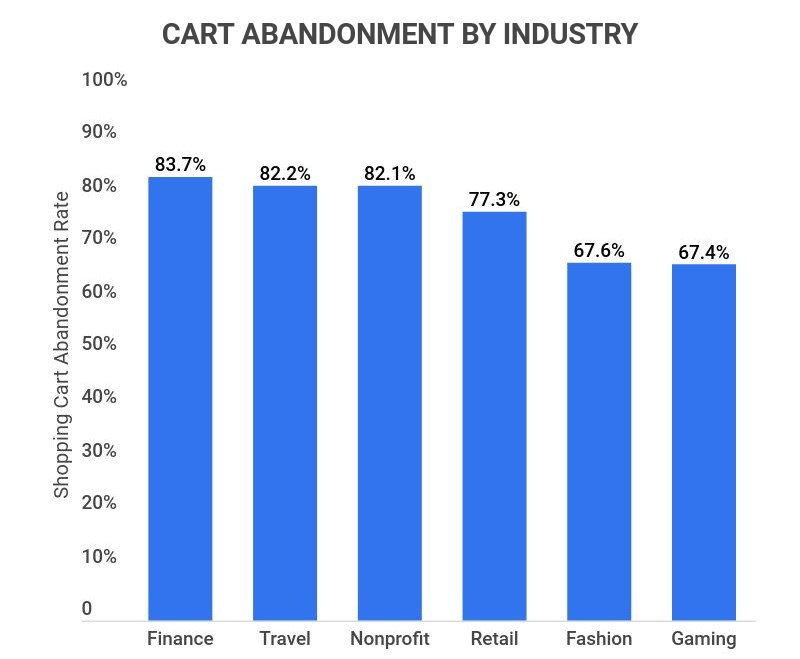
CAR Calculation:
CAR = (Number of Abandoned Carts / Number of Initiated Transactions) x 100
Example: If your online store has 500 abandoned carts and 1,000 initiated transactions, the Cart Abandonment Rate would be:
CAR = (500 / 1,000) x 100 = 50%
By regularly monitoring and analyzing the CAR, you can identify and resolve issues in the checkout process, such as user experience, payment options, and clear shipping/return policies, leading to reduced cart abandonment, higher conversion rates, more revenue, and improved customer satisfaction.
Average Order Value (AOV)
AOV is the average amount customers spend per purchase on your online store. This metric is crucial to assess the effectiveness of your marketing strategies, promotional campaigns, and overall customer experience.
AOV Calculation:
AOV = Total Revenue / Number of Orders
Example: If your online store generated $10,000 in revenue from 200 orders, the Average Order Value would be:
AOV = $10,000 / 200 = $50
Monitoring and analyzing AOV identifies opportunities to increase average customer spend per purchase. Tactics to improve AOV include offering upsells, cross-sells, bundle deals, or free shipping thresholds, leading to increased revenue and business growth.
Markting & Sales KPIs
- Site Traffic: Monitor the total number of visits to your eCommerce site to measure overall visibility and reach.
- Bounces: Assess the number of users who leave your site after viewing only one page, indicating potential issues with content or layout.
- Total Sales: Track daily sales profits to ensure you’re on track to reach monthly sales goals.
- Unsubscribes: Monitor the total number and rate of unsubscribes from your email list to identify potential issues with email content or frequency.
- Social Followers and Fans: Gauge loyalty, brand awareness, and engagement by tracking the number of followers on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Pinterest.
Customer Service KPIs
- Total Inquiries Outstanding: Track the number of active customer support issues to identify potential bottlenecks in your support process.
- Time to Respond: Measure the time it takes for your customer support team to respond to inquiries, which can impact customer satisfaction.
- Average Resolution Time: Assess the time it takes to resolve customer support issues, identifying areas for improvement in your support process.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: Monitor daily or monthly CSAT scores to understand customer satisfaction with their overall shopping experience.
Measuring E-commerce Success
There is more to measuring your eCommerce success than revenue. Let’s look at some additional factors that savvy marketers evaluate to make sure that their marketing strategies are succeeding.
- Repeat customers: Customers are coming back to your site for repurchases, this means they are increasing loyalty to your brand.
- Turnover changes to Leftover: Meaning, you not only break even with your monthly business expenses but have something (a profit) left over.
- Growing product assortment: When you can increase the different products and services you offer to your customers you are growing your overall business reach.
- Attracting corporate customers: This means more opportunities for bigger sales. Corporations tend to have larger budgets and spend more money per average purchase.
- Increased order value: The more customers spend more they become confident in your brand.
Conclusion: Launch. Measure. Optimize. Repeat.
eCommerce success goes beyond revenue. Here are key factors that smart marketers consider to ensure their marketing strategies hit the mark:
- Brand Loyalty: When customers repeatedly return to your site for more purchases, it’s a clear sign of growing brand loyalty.
- Profitability: It’s not enough just to break even with your monthly business expenses. When you see a profit or “leftover”, you know you’re on the right track.
- Expanded Reach: Expanding your range of products and services not only attracts new customers but also extends your overall business reach.
- Brand Confidence: Increased order value is another indicator of customers’ growing confidence in your brand.
Remember, while analyzing every bit of data can lead to paralysis, failing to measure at all may result in financial paralysis and, inevitably, disaster. Balance is key: measure what matters, optimize based on your findings, and keep iterating for success.
Resources for Learning More About KPIs and Tracking
- Google Analytics Academy: The Google Analytics Academy is a free Google Analytics course for beginners. The course shows new users how to create an account, implement tracking code, set up data filters, navigate the Google Analytics interface, generate reports, and set up dashboards and shortcuts. The course will also demonstrate how to analyze basic Audience, Acquisition, and Behavior reports, and set up goals and campaign tracking.
- Occam’s Razor by Avinash Kaushik: Occam’s Razor is the analytics blog by Avinash Kaushik. Avinash was the Sr. Director of Global Analytics and Digital Marketing Evangelist for Google, Co-Founder, and Chief Education Officer for Market Motive, and best-selling author of Web Analytics 2.0 and Web Analytics: An Hour A Day. You’ll find his posts categorized into a structure that will (hopefully) make it easy for you to discover new content, find answers to your questions, or simply wallow in some excellent analytics narratives. This is “the source” if you’re serious about KPIs.
- Kissmetrics: Kissmetrics is an analytics and conversion optimization platform that provides in-depth insights into customer behavior and KPI tracking.
- Shopify Analytics: If you’re using Shopify as your eCommerce platform, you can access their built-in analytics dashboard to monitor your store’s KPIs.
- Measurement School: A go-to YouTube resource, MeasureSchool offers tutorials on Google Tag Manager, Google Analytics 4, Google Data Studio, and more.
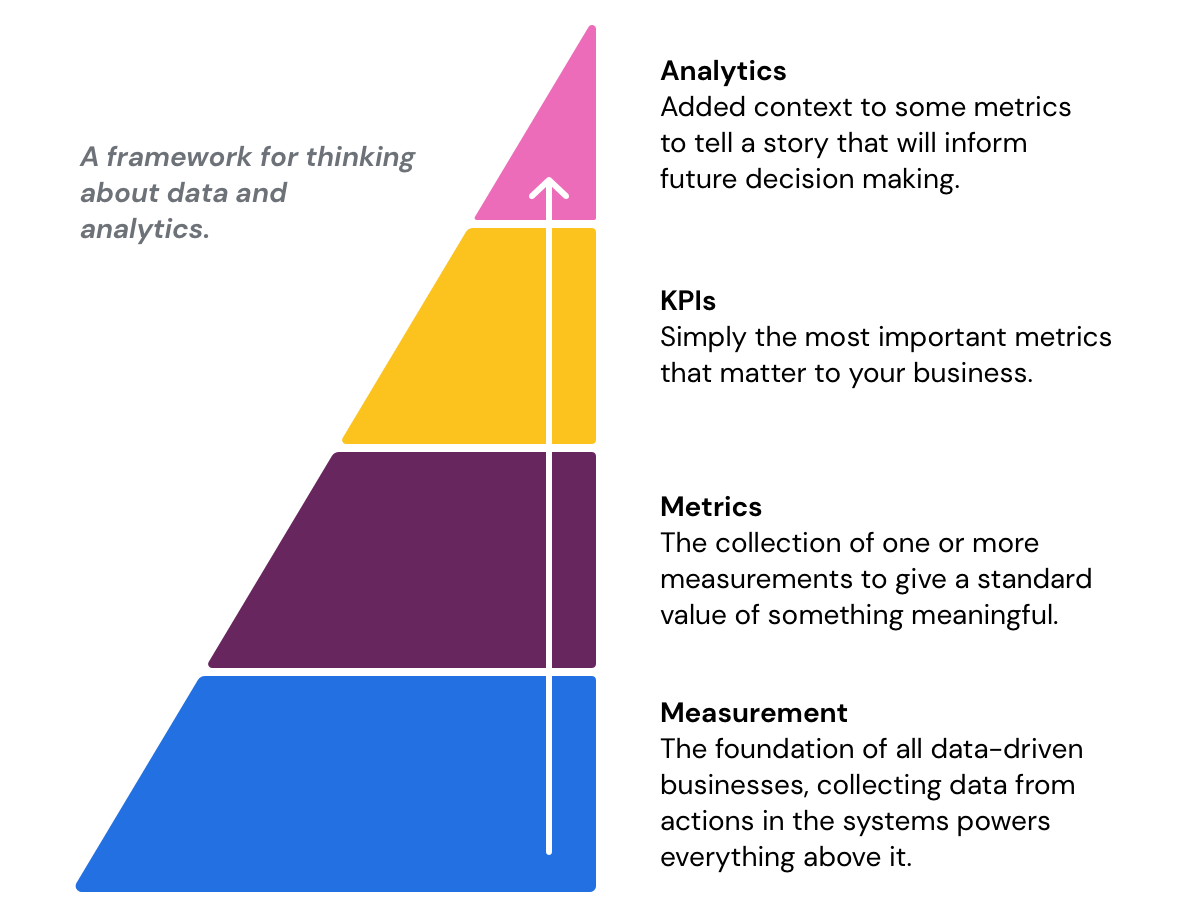
Analytics
Analytics, a broad term, involves the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data to unearth trends, patterns, and insights. It leverages various tools and methodologies, turning raw data into actionable information.
- Descriptive and Predictive Nature
Analytics serves a dual purpose: it’s descriptive, offering insights into past events, and predictive, forecasting future possibilities based on historical data and trends. This duality helps businesses understand performance contributors and pinpoint areas for enhancement. - Unveiling Complex Insights
By employing complex calculations, algorithms, and statistical models, analytics can delve deep into a business’s performance. Its spectrum of analyses is vast, ranging from customer segmentation and sentiment analysis to sales forecasting. - Specialized Skills Required
Executing analytics requires a distinct skillset, including data analysis, programming, and an in-depth understanding of a business domain. Experts such as data analysts and data scientists typically carry out these tasks. - E-commerce Analytics
E-commerce analytics focuses on a broad array of metrics related to online stores or e-commerce businesses. It aims to equip businesses with insights into online performance, customer behavior, and various facets of their sales and marketing efforts. With these insights, e-commerce businesses can make informed decisions, fine-tune their strategies, and ultimately elevate their performance and profitability.
Analytics versus KPIs
Analytics and KPIs are both crucial components of data-driven decision-making, but they serve different purposes and offer distinct insights:
- KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are specific metrics that measure the progress of a goal. They are typically measurable, relevant, attainable, time-bound, and actionable. For example, a KPI for a company that sells online products might be the number of new customers acquired each month.
- Analytics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to gain insights into what’s driving the performance. Analytics can be used to identify trends, patterns, and relationships in data that would not be apparent from simply looking at the data. For example, analytics could be used to determine which marketing channels are most effective at driving new customer acquisition.
In the example above, the number of new customers acquired each month is a KPI. It is a specific metric that measures the progress of the company toward its goal of acquiring new customers.
Analytics could be used to determine which marketing channels are most effective at driving new customer acquisition. This information could then be used to optimize the company’s marketing campaigns and improve its KPIs.
| Feature | KPIs | Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specific metrics that measure progress toward goals | The process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data |
| Purpose | To track progress toward goals and make informed decisions | To gain insights into an organization’s performance |
| Characteristics | Measurable, relevant, attainable, time-bound, actionable | Can be used to identify trends, patterns, and relationships in data |
I hope this example helps to explain the difference between KPIs and analytics.
5 Key Areas of E-commerce Metrics
It’s easy for e-commerce businesses to feel overwhelmed by the abundance of data available, sometimes defaulting to gut instinct-based decisions over data-derived insights. To simplify the process, we’ve broken key e-commerce metrics into five pillars, each representing a different stage in the customer lifecycle.
1. Discovery
The discovery phase is instrumental in learning about your audience and sparking awareness to direct potential customers to your online store. Google Analytics offers valuable demographic details about your visitors, such as age, gender, location, interests, and behavior, assisting you with the creation of user personas.
Essential Metrics for Increased Online Presence:
- Monitor email and social media engagement metrics, including reach, impressions, and engagement rates.
- Track organic search metrics, like search volume and keyword rankings will provide insights to help create advertising and content marketing strategies.
Understanding these metrics will help you enhance your e-commerce store’s visibility and boost potential product discovery.
2. Acquisition
The acquisition phase measures the consumer traffic in your store and the cost to secure those visitors. The investment in the discovery phase justifies itself when visitors arrive at your online store.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Marketing Performance:
- Track click-through rate (CTR) to assess the effectiveness of your ads or emails.
- Monitor cost per lead (CPL) to understand the investment needed to acquire a potential customer.
- Observe cost per acquisition (CPA) to know the expense of converting a potential customer into a sale.
Utilize these metrics to evaluate marketing campaign success and make informed decisions to optimize your acquisition strategies.
3. Conversion
After driving visitors to your e-commerce store, the next step is to convert them into customers. Unfortunately, not everyone who visits your store will end up clicking the add to cart button. What’s more, even those who click that button might change their mind and leave your website.
Key Metrics for Improving the Online Shopping Experience:
- Keep track of sales conversion rates to understand how many visitors are turning into customers.
- Monitor average order value (AOV) to gauge customer spending patterns per transaction.
- Check the cart abandonment rate to spot potential issues within the checkout process.
Regularly analyzing these metrics helps identify areas for improvement, devise strategies to increase conversions, and ultimately increase your overall e-commerce revenue.
4. Retention
Smart businesses recognize the value of loyal customers. Retaining customers reaps long-term benefits, and it’s always more cost-effective to keep customers than acquire new ones.
Important Metrics for Customer Retention:
- Monitor customer lifetime value (CLV) to assess the profit potential of a customer over their entire relationship with your business.
- Keep an eye on the customer retention rate (CRR) to measure your success at retaining customers over a specific period.
- Track the churn rate to understand how many customers stop doing business with you during a certain period.
Regular tracking and analysis of these metrics help in enhancing customer relationship management, developing strategies for customer loyalty, and increasing overall profitability.
 To give you an idea of how important customer retention is, research done by Frederick Reichheld of Bain & Company, revealed increasing customer retention rates by 5% increases profits by 25% to 95%.
To give you an idea of how important customer retention is, research done by Frederick Reichheld of Bain & Company, revealed increasing customer retention rates by 5% increases profits by 25% to 95%.
5. Advocacy
Once customers reach this stage, they evolve from regular shoppers into brand ambassadors.
Key Metrics for E-Commerce Success:
- Use the Net Promoter Score (NPS) to measure customer willingness to recommend your brand to others.
- Monitor newsletter subscriptions to gauge interest in your brand and its offerings.
- Measure participation levels in your loyalty programs to understand customer engagement and repeat business.
Regular monitoring of these metrics can help increase brand advocacy and contribute significantly to your success. The next step is to consider more advanced e-commerce analytics.
Google E-commerce Analytics
E-commerce data-driven decision-making is a cornerstone of success.
E-commerce analytics provide numerous benefits that help businesses stay ahead and create satisfying customer experiences.
- Data-driven product development: E-commerce analytics provides insights into consumer preferences, enabling businesses to develop products that cater to customer demands, thus increasing the chances of success.
- Efficient inventory management: Effective inventory management is critical for maintaining a seamless online store experience. E-commerce analytics helps businesses forecast, plan, and manage inventory levels, ensuring order fulfillment and timely reordering.
- Cross-sell and up-sell opportunities: E-commerce data can be used to implement retargeting strategies that focus on cross-selling and up-selling to existing customers, which is more cost-effective than acquiring new customers.
- Gathering user behavior data: By collecting and analyzing user behavior data, businesses can better understand customer demands, expectations, and pain points, allowing them to stay relevant and adopt a consumer-first mentality.
- Personalized shopping experiences: E-commerce analytics enables businesses to predict individual customer needs and offer relevant product recommendations, resulting in a personalized shopping experience that drives customer loyalty and sales.
- Engaging user experience: Analyzing customer data allows businesses to create engaging, frictionless user experiences that meet consumers’ evolving needs, leading to increased brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
- Optimized product portfolio: E-commerce analytics helps businesses identify best-selling products and underperforming items, enabling them to optimize their product portfolio and make informed decisions about product offerings.
- Maximizing return on ad spend (ROAS): By identifying effective ad campaigns and targeting the right audience, e-commerce analytics helps businesses maximize their return on ad spend, ensuring efficient use of marketing budgets.
- Satisfied customers: The ultimate goal of e-commerce analytics is to gather data that helps businesses understand and exceed customer expectations, resulting in satisfied customers and long-term brand loyalty.
Harnessing the power of data, businesses can optimize their product offerings, marketing efforts, and overall customer experience, ultimately driving growth and success in the e-commerce space.
Specific E-commerce Insights
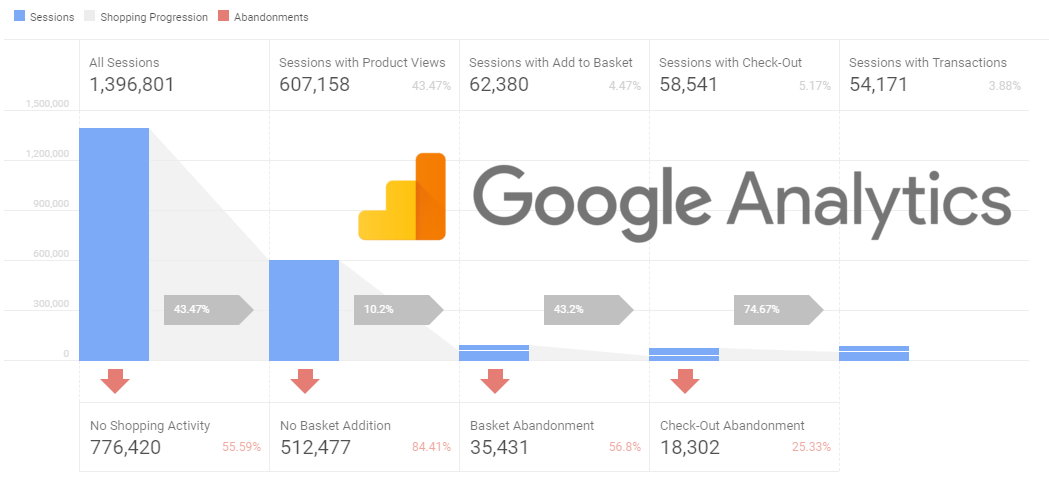
Insights from Enhanced E-commerce can be categorized into three groups: User behavior data, product data, and marketing data.
1. User behavior data
Enhance your online store’s performance with the Enhanced E-commerce advanced reports detailing user behaviors from browsing to checkout.
- Shopping Behavior Report is your guide to each stage 0f the sales funnel, detailing the customer journey on your site, and identifying areas for improvement.
- Checkout Behavior Report can identify and correct issues causing cart abandonment, improving the user experience and decreasing abandonment rates.
The insights gained from these reports will help you understand customer behaviors, spot trends, optimize user flows, and make informed decisions that can elevate conversions and boost revenue.
2. Product Data
Enhanced E-commerce reports help owners gather critical product performance insights. This data can be used to make informed decisions on product optimizations and marketing strategies.
- Product Performance Reports can capture sales and shopping behaviors. It provides data on product revenue, unique purchases, and refunds, along with details on product interactions like views, additions, and removals from the basket.
- Sales Performance Reports capture revenue data, including tax, shipping costs, refunds, and quantity of products sold, which can be tracked by transaction ID or date.
- Product List Performance Reports can improve cross-selling and up-selling strategies with insights into product list views, clicks, and click-through rates.
These reports will assist you in fine-tuning your product offering, creating effective pricing strategies, and planning targeted promotional campaigns to drive sales and improve customer satisfaction.
3. Marketing Data
Use Enhanced E-commerce tracking to measure your internal and external marketing efforts.
- Internal Promotion Report provides insights on internal promotion tools, such as banners, with metrics like internal promotion views, clicks, CTR, transactions, revenue, and transactions per internal promotion click.
- Order Coupon Report shows the performance of order coupons in terms of revenue, transactions, and average value.
- Product Coupon Report, similar to the order coupon report, offers insights related to product coupon performance in terms of revenue, unique purchases, and product revenue per purchase.
- Affiliate Code Report allows you to track the contributions of affiliate sites to your online store’s success, with metrics showing revenue, transactions, and average order value.
E-commerce Analytics Best Practices
Creating a competitive customer experience relies on embedding e-commerce analytics throughout the customer lifecycle. These five best practices will help you channel your focus and extract maximum value from e-commerce analytics:
- Consolidate marketing data: Pre-built data connectors can help you gather data from multiple sources and consolidate it into Google Sheets, Excel, or Google Data Studio. By consolidating marketing data, you will improve productivity, efficiency, and business agility.
- Understand the data: Collecting data is meaningless if you cannot understand it. Cross-channel reporting provides a holistic view of user behavior, enabling better decision-making and identifying areas for improvement.
- When to act: Use rule-based alerts for specific products, categories, or campaign performance. Custom alerts ensure you know the right time to act, helping you focus on successful strategies and eliminate underperforming campaigns.
- Automate e-commerce dashboards: Automating dashboards saves time and reduces the risk of errors. Setting reports to refresh automatically allows you to focus on data analysis and delivering value to customers.
- Share analytics: Centralized data shared with your team is essential for informed decision-making and contributes to business growth in the long run.
Ecommerce Aholic
Tools and Resources for Tracking and Analyzing Data
Google Analytics: A powerful and free web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic. You can use it to monitor KPIs such as conversion rate, AOV, and more. The tool also provides detailed insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and content performance.
Facebook Ads Manager: A platform for creating, managing, and analyzing Facebook advertising campaigns. It offers detailed reports on ad performance, audience demographics, and conversion tracking.
Google Data Studio: A free data visualization tool that allows you to create custom dashboards and reports using data from various sources, such as Google Analytics, Google Ads, and social media platforms.
Hotjar: A user behavior analytics tool that provides insights into how visitors interact with your website through heatmaps, session recordings, and feedback polls. This can help you identify areas for improvement in your website’s user experience.
Tableau: A powerful data visualization software that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards for analyzing your business data. It can connect to a wide range of data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and cloud services.
By investing your time in learning the right tools, you can harness the power of data to drive your business forward and ensure long-term success.
MeasureSchool