
Topics
Maximizing profitability is a central goal for any business. In this section, we will explore essential aspects of understanding costs, pricing products for profit and competitiveness, and identifying strategies for maximizing profitability. The goal is to ensure your financial success. In this section, you will:
- Gain clarity on the costs involved, including production, shipping, platform fees, and marketing expenses. It is essential to understand these foundational costs in order to create effective pricing strategies.
- Discover how to determine the best price for your products, considering factors like market trends, competitor pricing, and your target audience’s willingness to pay.
- Explore strategies such as optimizing your product catalog, improving design quality, implementing cost-effective marketing, and leveraging customer data.
By the end of this section, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools to price your POD products effectively and maximize profitability.
POD Costs
Choosing the right price for your products is essential for maximizing your profits. Follow these four steps to price your products Let’s examine key steps to pricing your products efficiently.
Step One: Product Cost
The cost of a product includes design cost, production cost, shipping, taxes, and any platform fees.
1. Design
Designs cost are the total expenses you incur on a product design for a product. There are several expenses to include when determining your design cost.
First, let’s consider the cost of the design. There are several ways to determine the value of product designs, here are a few to get you started:
- Outsourced Product Designs
When outsourcing design services, it’s important to factor in design costs. You can do this by dividing the price paid to the designer by the number of products you plan to sell. This is especially crucial for limited edition or limited-time designs, as it directly affects your profit potential.
DESIGN COST PER PRODUCT = DESIGN PRICE ÷ PLANNED SALES
- Uncertain Product Sales (i.e., Seasonal Products)
If you’re unsure about the number of designs you’ll sell, calculate how many units you need to sell at your chosen price to break even, considering your profit margin. This helps you know the minimum sales target and adjust your profit margin if necessary.
MINIMUM ORDERS TO SELL = DESIGN PRICE ÷ PROFIT MARGIN
- In-house Product Designs
If you create your own designs, it’s tempting to disregard design costs. However, your time is valuable, so make sure you account for it by setting a realistic hourly rate for your work and adding it to the product cost.
DESIGN PRICE = HOURLY RATE x HOURS DESIGNING
2. Production
Production cost is included in the price you pay for each item. You can usually find the supplier’s product pricing on their ‘product page’ or when adding products to your store. Your cost depends:
- Production method
- Print placement
- Color and Size
- Fulfillment location
3. Shipping
Although POD suppliers typically handle shipping, it’s an extra cost for your customers. You should consider what shipping rates to offer your customers and ensure the fee covers your supplier’s actual rate. Shipping prices vary based:
- Product size and weight
- Fulfillment location and shipping destination.
RETAIL PRICE W/FREE SHIPPING = RETAIL PRICE + SHIPPING RATE
NOTE: You only need to add a shipping fee if you process and deliver orders yourself. Delivery companies may charge you a specific rate based on the product type, arrival, destination, shipping method, etc. There are two ways to add this cost:
- Charge your customers extra for shipping and do not add to the product’s cost. It helps the price decrease and impresses customers at first sight.
- Offer a free shipping service by incorporating shipping rates into your product base price, making your products more attractive to customers. Customers are 4 to 5 times more likely to buy something if you offer them free shipping. You can do that by including the rates in your product base price, so you don’t have to pay for shipping out of pocket.
4. Taxes
Taxes may apply depending on your customer’s location. Examples include Sales Tax in the US and Canada, VAT in the EU, UK, Norway, and Liechtenstein, and GST in Australia and New Zealand.
![]() You may also be responsible for collecting taxes from your customers, so consult a tax specialist to understand your tax obligations and factor them into your product price.
You may also be responsible for collecting taxes from your customers, so consult a tax specialist to understand your tax obligations and factor them into your product price.
 When you are operating a dropshipping business, you have the potential to make sales in every State – that’s a lot more complicated than a brick-and-mortar. For more information about taxation and dropshipping, I suggest reading this Printful article: Beginners Guide to Dropshipping Sales Tax by Nora Inveiss.
When you are operating a dropshipping business, you have the potential to make sales in every State – that’s a lot more complicated than a brick-and-mortar. For more information about taxation and dropshipping, I suggest reading this Printful article: Beginners Guide to Dropshipping Sales Tax by Nora Inveiss.
5. Platform Fees
Selling online may require using a platform. Consider their cost in your calculations.
| PLATFORM | PLAN & MONTHLY FEE |
| Shopify +$0.30 transaction |
|
| WooCommerce +$0.30 transaction |
|
| BigCommerce +$0.49 transaction |
|
| Wix + $0 transaction |
|
| Squarespace |
|
Step Two: Profit Margin
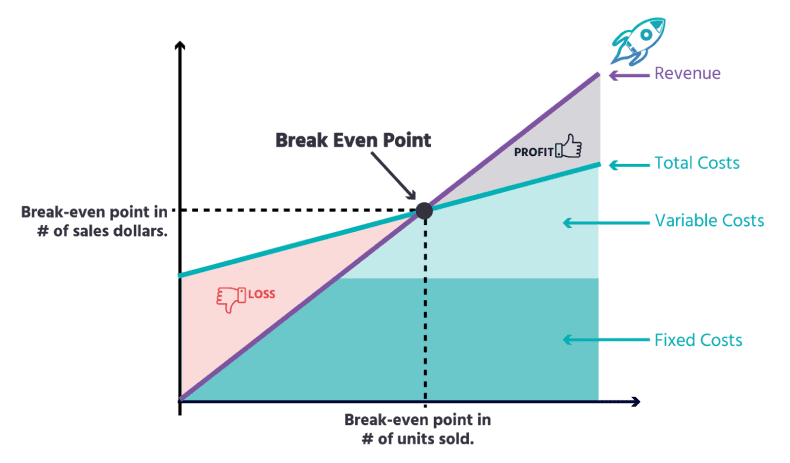
Consider the overall market and ensure your price falls within an acceptable range for your target audience. If your retail price is significantly higher than competitors, making sales could be difficult.
At the same time, remember the effort you put into your store and avoid setting your margin too low. If your profit margin doesn’t justify the time and effort invested in your store, reassess your margin or your store’s efficiency.
$ PROFIT = PRODUCT COST x PROFIT MARGIN (%)
This step allows you to experiment and be creative by adjusting your profit margin to match or surpass competitors and explore various pricing strategies.
RETAIL PRICE = PRODUCT COST + PROFIT MARGIN
Step Three: Consider Additional Expenses
Some platforms, like Shopify, have fixed costs, while others, like Etsy or eBay, charge a percentage of sales and listing fees. Payment processors like PayPal charge transaction fees. There are also additional fixed costs to consider such as monthly e-commerce platform subscriptions, advertising budgets, internet subscriptions, etc.
Divide your total monthly expenses by your profit margin to determine how many products you need to sell per month to break even.
MINIMUM ORDERS PER MONTH = MONTHLY COSTS ÷ PROFIT MARGIN
If the minimum number of products to sell or the retail price becomes unrealistic, you must either adjust your costs or reduce your expenses. Budget balancing is an ongoing process, so be prepared for that.
Step Four: Review Your Prices Often
Product pricing isn’t a one-time decision… While it’s essential to ensure your prices cover all your costs and reward your hard work, experimenting with different pricing strategies can be an effective selling tactic.
EXERCISE
Let’s walk through the steps and estimate the cost to sell a standard T-Shirt.
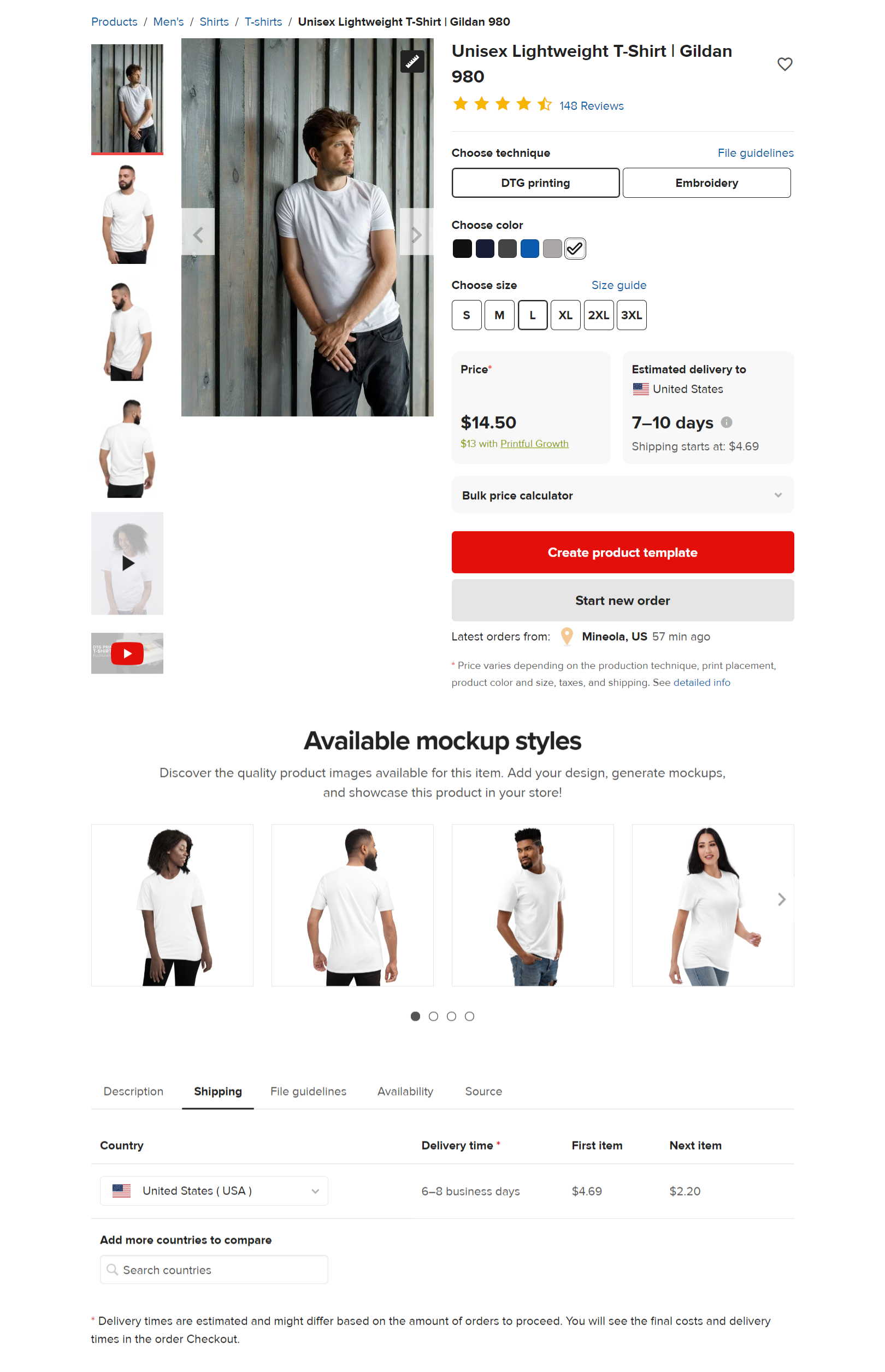
I will be using Printful as a supplier and Shopify as my storefront. My intended audience is located in Nevada, and I want a 20% profit margin.
—
STEP 1: Product Cost
1 Design Cost
Our product is the Unisex Lightweight T-Shirt | Gildan 980 (Printful) T-shirt with a simple text print design. I will be the designer and it will take me 15 minutes. I want to get paid for my work (time investment), so I will include my time and calculate the design cost.
I’ll set my hourly rate at $28/hour and multiply that by the time spent on the design, which is 1/4 of an hour. This amounts to $7.00 for this design.
DESIGN PRICE = HOURLY RATE x HOURS DESIGNING
$7.00 (design price) = $28.00 (hourly) x 1/4 hour (hours designing)
Assuming I could sell 10 shirts with this design, the cost per design would be 0.70¢.
DESIGN COST PER PRODUCT = DESIGN PRICE ÷ PLANNED SALES
$0.70 (cost per design) = $7.00 (design price) / 10 (planned sales)
—
2 Production Cost
The T-Shirt is simple, but I need to check for colors and sizing price variations.
This T-Shirt has multiple size price points: S-XL: $14.50, 2XL: $16.50, and 3XL: $18.50.
To make my calculations similar, there are four ways to approach size price differences when determining production cost:
- I could price each size or size group as separate products which isn’t always ideal.
- I could calculate the product cost based on the most expensive size. In this case, that would be $18.50. If a customer purchases a shirt in size S to XL ($14.50) I gain an extra $4.00, and a 2XL (16.50) I gain an extra $2.00. If they buy a 3XL, I cover my costs exactly. This method works if I don’t focus on low retail prices as my selling point.
- I could calculate the product cost based on the least expensive size. If a customer buys a size XS to XL, I cover my costs exactly. If they purchase a 2XL, I lose $2.00, and a 3XL, I lose $4.00, reducing my profit but keeping my prices low.
- I could calculate the average cost of all sizes. I’ll add up all the costs and divide them by the number of sizes I offer. In this case, the average cost is $15.50. Now, every time I sell a size S to XL (+ $1.00), a 2XL (- $1.00), and 3XL (- $3.00).
AVERAGE COST = (S+M+L+XL+2XL+3XL) ÷ VARIATIONS
$15.50 = $14.50+$14.50+$14.50+$14.50+$16.50+$18.50 / 6
To simplify, I’ll use option 4 and use $15.50 before taxes as the cost.
—
3 Shipping Cost
Reviewing Printful’s Shipping information, they charge $4.69 for the first item and $2.20 for the next item.
To simplify, I’ll use $4.69 shipping and add that fee to my production cost. Since I’m including the shipping cost in my product cost, I can offer free shipping to my customers.
—
4 Taxes
I plan to sell this shirt exclusively in Nevada. Even though I don’t have a physical storefront or economic nexus in Nevada, the supplier (Printful) does and they will charge me sales tax on every order (states Printful charges sales tax). Nevada is part of the Streamlined Sales and Use Tax Agreement, so I can use a 6.85% sales tax rate.
Sizes S to XL: $14.50 x 6.85% = $0.99, 2XL: $16.50 x 6.85% = $1.13, and 3XL: $18.50 x 6.85% + $1.27.
To simplify, I’ll use the average shirt cost of $15.50 to calculate the sales tax ($15.50 x 6.85%), resulting in $1.06 in taxes added to my product cost.
—
5 Platform Fee
I’m using Shopify, and they charge a $0.30 order fee and a 2.9% transaction fee.
Let’s calculate our total costs:
Design Fee: $0.70
Product Cost: $15.50
Shipping: $4.69
Taxes: $1.06
Shopify Order Fee: $0.30
SUBTOTAL: $22.25
To calculate Shopify’s 2.9% Transaction Fee, I need to determine my Tee’s sale price. Since I want a 20% margin, I can guesstimate a retail price of around $27.00 [Step 2].
$27.00 x 2.9% = $0.78 transaction fee.
$22.25 (Subtotal) + $0.78 (Transaction Fee) = $23.03
TOTAL: $23.03
===
STEP 2: Profit Margin
Retail pricing needs to include profit margin, but you can’t determine profit margin until you know the actual retail price…
To determine the retail price for my T-Shirt, I’m going to calculate my profit margin first:
I want a 20% profit margin.
Cost Summary Total [from 1.5] = $22.25 (without the Shopify 2.9% transaction fee).
$22.25 + 20% margin ($4.45) = $26.70
Let’s round up (for calculating actual Shopify fee and profit margin): $27.00 estimated retail price.
RETAIL PRICE = PRODUCT COST + PROFIT MARGIN
$22.25 + 20% ($4.45) = $26.70 (min retail price)
===
STEP 3: Consider Additional Costs
I’m selling the T-Shirt on Shopify which has a $39.00 monthly subscription price. I also have monthly advertising and/or social media marketing costs to consider. Let’s total this up:
Shopify Basic Subscription: $39.00/month
Advertising/Marketing: $300.00/month
Subtotal: $339.00/month
With monthly costs totaling $339.00 and a $4.45 profit margin (20%), I need to sell at least 77 shirts per month to break even.
MINIMUM ORDERS PER MONTH = OTHER MONTHLY COSTS ÷ PROFIT MARGIN
$339.00 (monthly costs) / $4.45 (20% profit margin) = 76.2 (minimum orders per month)
The retail price must include all costs and the profit margin. Product costs may include graphic design, production, shipping, taxes, and platform order fees. Feel free to adjust your profit margin based on your preferences and competitors, but don’t forget to account for additional costs and calculate the minimum number of orders needed to cover expenses.
===
STEP 4 Review Pricing
Production costs may vary due to factors like customer location (shipping), taxes (location), and other variables (product sizes, etc). Adjust your retail price depending on production expenses, competition, seasonal trends, or the pricing strategy you choose.
===
Example: T-Shirt
Product cost
| Cost | Components | Value |
| Design | In-house design
|
Price per design: $7.00 |
| Production | Unisex Lightweight T-Shirt | Gildan 980 (Printful) | $15.50/order |
| Shipping |
|
$4.69/order*
*First item $4.69, next item $2.20 |
| Tax | Nevada Streamlined Tax Agreement | $1.06 |
| Platform Fee | Shopify $0.30 Order Fee 2.9% Transaction Fee |
$0.30 $0.78 |
| Total | $23.03 |
With a desired profit margin of 20%, the profit is $4.45, and the minimum retail price of the T-Shirt is $26.70.
Other monthly costs
| Cost | Components | Value |
| Website creation and platform charges | Domain: Shopify Basic Plan
Hosting: Shopify |
$39.00/Month
Free |
| Advertising/Marketing | Ads or Social Media | $300.00 |
| Total | $339.00 |
Our store only sells T-Shirts and the additional monthly costs total $339.00. Using the 20% profit of $4.45, the minimum number of orders per month is around 77 orders ($339.00 / $4.45).
Example: Coffee Mug
Let’s practice another example using a personalized mug.
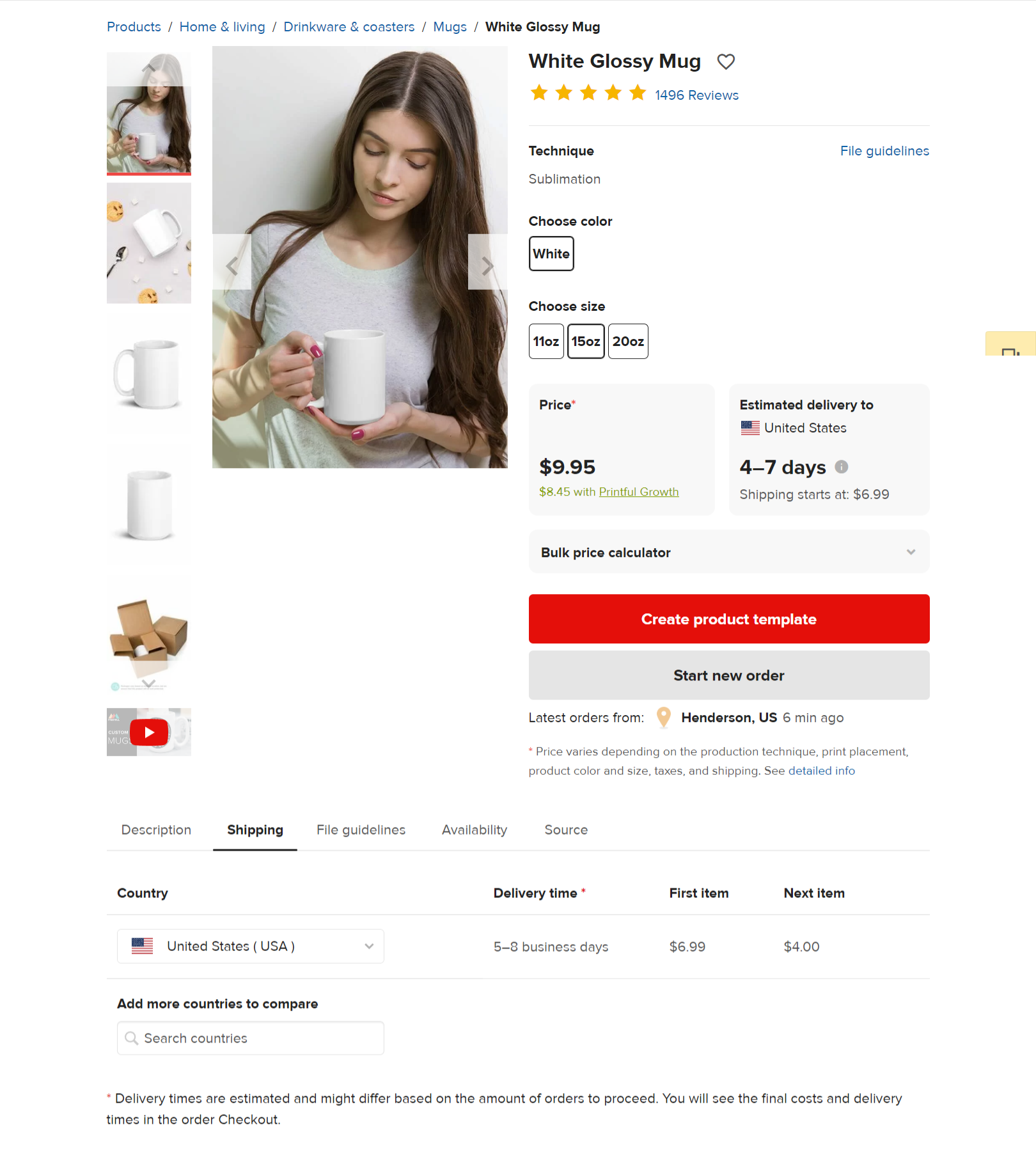
Product cost
| Cost | Components | Value |
| Design | In-house design
|
|
| Production | White Glossy Mug 15oz (Printful) | $9.95/order |
| Shipping |
|
$6.99/order*
*First item $6.99, next item $4.00 |
| Tax | $1.00 | |
| Platform Fees | Shopify $0.30 Order Fee 2.9% Transaction Fee |
$0.30 $0.73 |
| Total | $19.67 |
With a profit margin of 20%, the profit is $3.93, and the minimum retail price of the mug is $23.60.
Other monthly costs
| Cost | Components | Value |
| Website creation and platform charges | Domain: Shopify Basic Plan
Hosting: Shopify |
$39.00/Month
Free |
| Advertising/Marketing | Ads or Social Media | $300.00 |
| Total | $339.00 |
This store only sells personalized mugs, with the additional monthly costs totaling $339.00. Using the 20% profit of $3.93, the minimum number of orders per month you have to sell is 86.3 orders ($339.00 / $3.93).
Pricing Strategies
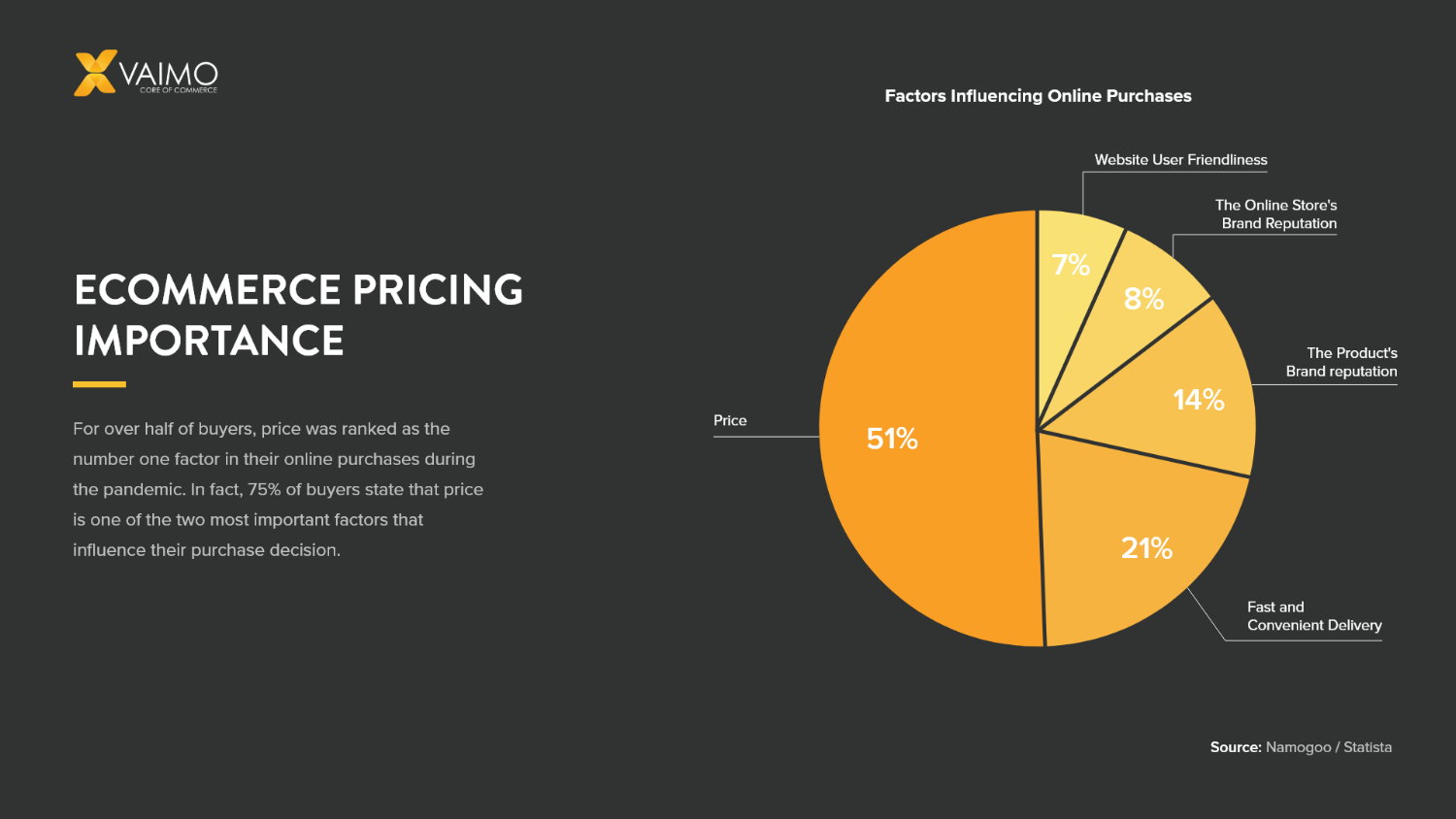
In addition to calculating costs and desired profit margins, you also need to create a pricing strategy. Study your competitors’ prices, making sure you price competitively. If you price too high, you may lose customers, but pricing too low might not sustain your business.
Review the price strategies below and determine which one(s) may work for you:
Market / Competition-Oriented Pricing
Align your pricing within the market range. Gauge the average price and potential range by comparing your products with competitors.
| Pros | Cons |
| Works in highly competitive markets. | May damage the brand. |
| Attracts price-sensitive customers. | Difficult to differentiate in the market. |
Choose from three main tactics:
- Above the market average: Enhance the shopping experience with gifts or higher-quality visuals.
- The same as the market: A safer bet, attracting a broad audience while maintaining profitability.
- Below the market average: Attract customers with lower prices but beware of underpricing.
Example
Let’s say you’re running a t-shirt business and you’ve noticed that most good-quality t-shirts in your target market are priced at $20. To make your t-shirts even more appealing, you decide to price them at $19, just a little bit less than the others. This way, your customers get a great deal without sacrificing quality, and you can still make a good profit while winning over the bargain hunters out there.
Demand or Dynamic Pricing
Adapt your product price based on demand. If demand fluctuates, or additional costs emerge, adjust your pricing accordingly.
| Pros | Cons |
| Excellent for seasonal products. | Hard to predict demand. |
| Increases profit in peak season. | May appear unethical or manipulative. |
Example
Imagine you have a t-shirt business and you’ve just released a limited-edition design that’s getting a lot of buzz. As demand for this trendy t-shirt goes up, you decide to raise the price a little to capitalize on the hype. On the flip side, if you have a seasonal t-shirt that isn’t selling as well during the off-season, you can lower the price to entice more buyers. This way, you’re always staying in tune with your customer’s wants and needs while maximizing your profits. Pretty clever, right?
Anchor Pricing
Anchor pricing is a common tactic that leverages customers’ perception of value by setting an imaginary anchor price, then offering a lower discount price to appeal to deal-seeking customers.
| Pros | Cons |
| Create a perceived value. | Difficulty offering higher prices. |
| Improves customer satisfaction. | May lower profit in the long term. |
Example
You have a t-shirt business, and you want to promote your premium t-shirts. You could display a regular t-shirt priced at $30 alongside your premium t-shirt, which is priced at $35. By doing this, you create an anchor price of $30, making the premium t-shirt appear as a better value, as it’s only $5 more for the added quality and features. This comparison encourages customers to perceive the premium t-shirt as a more attractive option, ultimately leading to increased sales of the higher-priced item.
Discount Pricing
Similar to Anchor Pricing, start with a higher price, then have frequent sales to attract bargain shoppers, especially during popular e-commerce events like Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and Back-to-School. Try to leave room in your margins for future discounts without dipping into your pocket to cover expenses.
Offering discounts and sales can be an effective way to clear out old inventory. Be strategic with your promotions, and make sure they align with your overall business goals and pricing strategy.
| Pros | Cons |
| Quick market share gain. | Challenging to increase future prices. |
| Improves customer satisfaction. | May cause price wars. |
Example
You have a t-shirt business and you want to drum up some excitement around your brand. To do this, you decide to launch a weekend sale where customers can snag their favorite t-shirts at 20% off. This limited-time offer creates a sense of urgency, encouraging people to buy now before the deal ends. Not only does this help you sell more t-shirts in the short term, but it can also introduce new customers to your brand and create a buzz that keeps people talking long after the promotion is over. It’s a win-win for everyone!
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is often used for new brands entering the markets or an entirely new product in a pre-existing market.
| Pros | Cons |
| Quickly gain market share for new brands. | Challenging to increase prices in the future. |
| Attract new customers. | May cause price wars. |
Promotional Pricing
Established brands will temporarily offer products at a discounted price to attract customers and boost sales of existing products.
| Pros | Cons |
| Quickly generate sales for existing brands or products. | Challenging to increase future prices in the future and retain new customers. |
| Quickly attract new customers based on price. | May cause price wars. |
Example
Examples of promotional pricing include BOGOF (buy one get one free), seasonal sales promotions, discounts, and flash sales. Examples of penetration pricing include an online news website offering one month free for a subscription-based service or a bank offering a free checking account for six months.
Price Testing
Find your product’s pricing sweet spot by testing different price options.
Split Testing
Test different price points to determine the best-performing one. By comparing the performance of two or more price points, you can identify the optimal price for your products.
Example
You’ve got a t-shirt business and you’re not quite sure how much to charge for your latest design. To figure it out, you could do an A/B price test. You offer the same t-shirt to two different groups of customers, but you charge Group A $25 and Group B $30. After a while, you check out the results and find that more people from Group A bought the t-shirt. Looks like $25 is the way to go! By testing different prices, you can get to know your customers and find the perfect balance between affordability and profitability.
Price Elasticity
Understand how sensitive customers are to price changes, helping you make informed decisions about how to adjust your prices to maximize revenue.
Example
You’ve got a t-shirt business and you want to know if a price change will have a big impact on sales. So, you increase the price of your popular t-shirt from $20 to $25 and keep an eye on what happens. If sales hardly change, it means your t-shirt has a low price elasticity, meaning your customers don’t mind paying a bit more for it. But if sales drop significantly, that means your t-shirt has a high price elasticity, and your customers are pretty price-sensitive. Knowing this helps you make smarter pricing decisions and keeps your customers happy!
Value-Based Pricing
Set your product’s price according to its value, rather than costs or competition, to attract customers willing to pay a premium for value-aligned products.
Perceived Value
Perceived value is the worth that a customer assigns to a product based on their perception of its benefits and costs. Value-based pricing involves setting prices based on the perceived value of your products, rather than simply calculating the cost of production plus a profit margin.
Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation involves dividing your target market into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as demographics, interests, or buying behavior. By understanding the needs and preferences of different customer segments, you can tailor your pricing strategy to better meet their expectations and maximize profitability.
Example
You’re running a t-shirt business and you’ve created a high-quality, eco-friendly t-shirt made from sustainable materials. You know your target customers are environmentally conscious and appreciate the extra effort you’ve put into making a responsible product. So, instead of pricing your t-shirt based on what others are charging, you set the price at $30, which is higher than average, but reflects the true value and benefits your customers get from your eco-friendly t-shirt. By focusing on the value, you can attract the right customers who are willing to pay a premium for a product that aligns with their values.
Psychological Pricing
Use psychology to make prices more appealing.
Charm Pricing
Setting prices just below a whole number (e.g., $19.99 instead of $20). This strategy can make your products appear more affordable.
Price Anchoring
Display a higher reference price alongside your actual selling price, creating the perception of a good deal or a significant discount. This strategy can increase the perceived value of your offer.
Example
You have a t-shirt business, and you’ve got an awesome new design that you want to sell for around $20. Instead of pricing it exactly at $20, you decide to use psychology pricing and set the price at $19.99. Even though it’s just a penny less, our brains tend to focus on the first number we see, which in this case is 19 instead of 20. This little trick makes the t-shirt seem like a better deal, and customers feel like they’re getting more value for their money. It’s a simple yet powerful way to boost sales and make your prices more appealing!
Conclusion
Optimize your pricing structure with strategies like price testing, value-based pricing, promotional pricing, and psychological pricing. These approaches will help you attract customers, maximize profitability, and remain competitive in the market.
Strategies for Increasing Profitability

Boost your profitability with strategies like upselling, cross-selling, product differentiation, and building customer loyalty. These strategies not only increase your average order value but also grow your business.
Upselling
Encourage customers to buy higher-priced, upgraded versions of the products they’re interested in. This not only adds value for them but also boosts your revenue.
Example
Offer your customers a premium t-shirt made with extra-soft, organic cotton, priced at $25 instead of the basic Tee at $15.00. Highlight the benefits of the premium t-shirt, like its superior comfort and eco-friendliness, making it a more attractive choice. By showing the added value of the premium t-shirt, you give your customer a reason to consider spending a little more, resulting in a win-win for both of you!
Cross-Selling
Recommend complementary products to customers, enhancing the overall shopping experience while increasing your sales.
Example
As a customer adds a stylish Tee to the shopping cart, suggest a matching hat or stylish tote bag to go with their purchase. These additional items create a personalized and enjoyable shopping experience while increasing the total sale amount.
Bundles
Group multiple products together at a special combined price, giving customers a discounted price compared to purchasing each item individually. This strategy encourages customers to buy more items, increasing your average number of items per order.
Example
Create an irresistible offer for your customers by bundling a trendy t-shirt, matching hat, and stylish tote bag for $45. This deal encourages customers to buy the whole bundle, adding value to their purchase, and giving them a positive experience with the extra value they’re getting.
Product Differentiation
Offer options for custom colors, graphics, or text to create a memorable experience and command a premium price. This approach not only drives sales but also helps you establish a strong brand identity that sets you apart from the competition.
Unique Designs and Customization
Offering unique designs and customization options are fantastic ways to achieve product differentiation, making your brand stand out in a crowded market. These exclusive features add value to your products, attracting customers who appreciate the uniqueness and are willing to pay a premium for it. As a result, you’ll not only increase sales but also establish a strong brand identity that distinguishes you from the competition and can also allow you to charge a premium price for your products, increasing your profit margins.
Example
You have a coffee mug business, and offer your customers the option to personalize their mugs with custom text printing (names). Not only do you create a personalized gift and memorable shopping experience, but these added personalizations can command higher prices too.
Niche Markets and Target Audiences
Differentiate your products by focusing on specific audiences, like dog lovers. Cater to their unique interests to boost your brand recognition and develop a customer base willing to pay a premium for products that resonate with their interests.
Example
You focus your shop on dog lovers, creating unique, fun, and heartwarming designs featuring various dog breeds and witty sayings that resonate with this audience. By catering to their interests (not yours), you have less resistance to connecting with your target audience.
Customer Loyalty
Reward dedicated customers with incentives like points, discounts, or exclusive perks. By showing appreciation for their ongoing support, you not only strengthen your relationship with loyal customers but also encourage them to continue choosing your brand over competitors.
Example
Your rewards program earns points for every dollar spent on your products. As customers accumulate points, they can redeem them for discounts, freebies, or even limited-edition designs exclusive to members. You might also offer special perks, like early access to new collections or personalized recommendations.
Conclusion
Incorporating sales strategies into your business enhances profitability and ensures long-term success. Continuously evaluate and adapt your approach based on customer feedback and market trends to stay competitive and keep your customers engaged.