Google AdWords account structure is essential in creating effective campaigns. If there is one thing in the class to pay attention to, it’s properly setting up your account for success.
Why?
Good account organization helps you make changes quickly, target your ads effectively, and, ultimately, reach more of your advertising goals. By creating well-structured campaigns by theme or product, you’ll get more than just an account that’s easy to manage and keep organized: you’ll also have sets of ads and keywords that are directly related to each other, which helps improve your Quality Score and lower your advertising costs.
If you fail at organizing your account in the beginning, it can be a nightmare to reorganize an account later. Sometimes you lose valuable data which makes it hard to understand what was performing well and what didn’t sell.
Google Adwords Account Structure
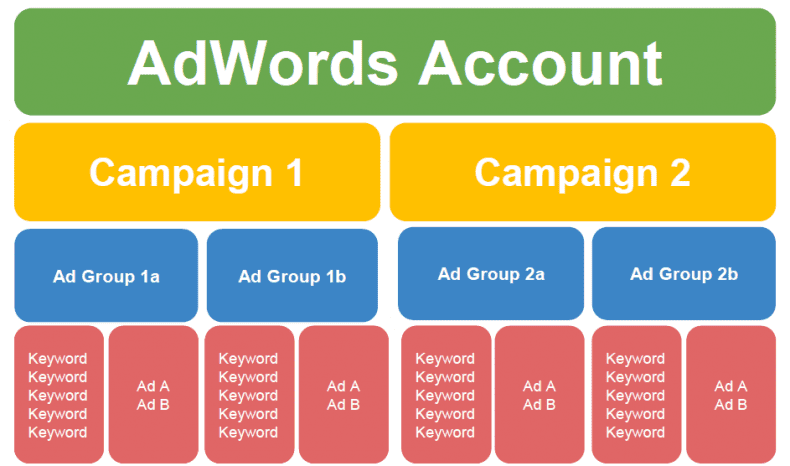
AdWords is organized into three layers: account, campaigns, ad groups.
1. Account Level
At the account level, you will set up business information and billing. If you have more than one location that requires separate billing, you will want to set up two separate accounts. If these accounts will be very similar, you can build one to completion and then use AdWords Editor to copy the campaign to the second account.
![]() If you are going to manage ad accounts for others, you can use a MCC (My Client Center) account – but we are not going to get into that in this course . You can read more about MMC’s here.
If you are going to manage ad accounts for others, you can use a MCC (My Client Center) account – but we are not going to get into that in this course . You can read more about MMC’s here.
2. Campaign Level
Most smaller/local businesses will not require a large number of campaigns. However, the more services or products you offer, the more campaigns you will need.
Here are the things that you will need separate campaigns for:
- Different location targeting
- Different service offerings (a landscaper who does both design and construction would need a design campaign and a construction campaign)
- Different ad scheduling
- Any campaigns that are different types (Search, Display, Remarketing, Call-Only, Video, GMail)
3. Ad Group Level
Ad Groups are the most important part of the campaign structure. A simple way to remember ad groups is think of them as keyword groups (but call them Ad Groups).
It is essential that you keep the list of keywords in each had group very closely related. Each ad group will be sending those keywords to the same ads and the same landing pages. This means that you have to include each keyword in the ad and use it multiple times on the landing page if you want a high quality score.
It is very difficult to do this when your list of keywords for an ad group is large. That is why it is best to segment the keywords into several close related ad groups.
Relevancy is the Key to Success
A well-structured account consists of separate campaigns for each of your product lines, general themes, or types of services you offer. Each of those campaigns, in turn, consists of tightly themed ad groups that focus on one specific product, service, or theme. Each ad group should contain specific keyword lists that relate directly to the associated ad text.
The more specific and the more relevant you keep your keywords within your to your ad groups, the easier it will be to manage and optimize your campaigns.
Best Practices in Structuring Campaigns
Let’s talk about some quick best practices…
Be Specific
It is always better to start out by being too specific versus too broad.
Consider creating several ad groups that are very targeted. Then, if you’re not getting enough traffic (however, research shows that the traffic volume is there), you can start loosen up those targeting limitations.
Basic Setup
What’s the best way to start? Truthfully, it dependents on your specific business and what your goals are.
If you need something to aim for and you have a limited budget – the best accounts are always organized:
- By creating a campaign
- That contains several ad groups
- Within those ad groups have 2-3 ads
- Using a maximum of 10-15 keywords within each ad group
- Beyond 10-15 keywords, your ad groups quickly become irrelevant and your keywords will not be close enough matched with your ad text to perform well
- Always have 2-3 ads to split test, watch them closely
- Always have two to three ads running – don’t just start off with two to three ads and then get down to one that’s your best performer
- Don’t stop there – always have two to three combinations
Top Three Tips For Structuring Your Account
1. Organize your campaign to mirror your website
A good rule of thumb for creating an effective campaign structure is to mirror your website’s structure. By creating campaigns and ad groups around a specific theme or product, you can create keyword lists that directly relate to the corresponding ad text, and ads that link directly to that product’s page in your website.
For example, a furniture store’s website is likely to have different sections for each type of product, like bedroom furniture and dining room furniture. The website might also have separate sections or pages for each specific product, like a certain bed or model of table.
![]() Here’s an example of good account structure:
Here’s an example of good account structure:
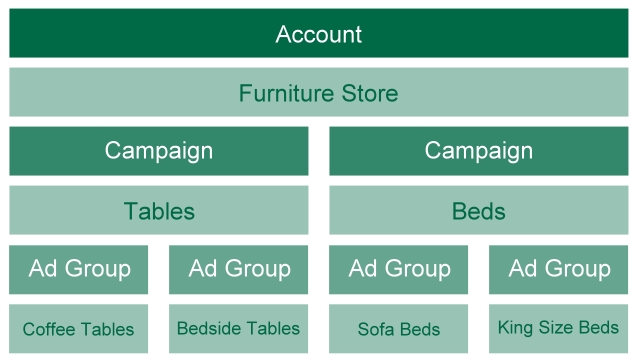
- The account contains everything relating to the furniture store.
- The campaigns are organized around broad product areas (the categories of furniture as a customer might group them).
- Each campaign contains several ad groups that focus on one specific product (like tables and beds).
This format can be changed to match your business and the scope of your advertising. For example, if you sell many types of beds, you can have a “Beds” campaign with ad group themes like “Bunk beds,” “Queen size beds,” and “Sofa beds.” Or, if you sell only one product or service, you can create a simple campaign structure around that product. For example, if you sell only lamps, you can create several ad groups based on descriptive themes like “beaded lamps” and “modern lamps.”
2. Create separate campaigns for multi-region advertising
If your business serves several areas, you might create a separate campaign for each location. For example, if you have a store in Las Vegas, Nevada and one in Paris, France, set up two separate campaigns, each targeting one of those locations. Each campaign should be translated to the local language and should emphasize that your services or products are available in that country.
![]() Examples
Examples
- The campaigns mentioned above that target USA and France should have ads in English and French, respectively.
- Local businesses such as furniture stores, real estate developers, or car dealerships may create a campaign for each region, and within each campaign, create a different ad group for each city or metropolitan area they cover. If you’re running a promotion in a specific city, you might create a campaign targeting that city only.
3. Use AdWords Editor to manage your campaigns
Tool: AdWords Editor is a free Google application for managing your AdWords ad campaigns. You can use it to make changes to your account quickly and conveniently, whether you’re editing one keyword or adding hundreds of text ads.
Other benefits:
- Add, edit, and delete campaigns, ad groups, ads, keywords, and placements.
- Make large-scale changes quickly.
- Perform advanced searches and edits.
- Sort and view performance statistics.
- Copy or move items between campaigns, ad groups, and accounts.
- Export a snapshot of your account for archiving or sharing.
You can download the AdWords Editor here.