
Week One Objectives:
- Learn how to turn on and turn off the computer. Executing this move. Understanding how and why it is important to turn off the computer properly.
- Learn the parts of the computer and what they are called. Learn what a peripheral is and why.
- Learn the difference between “software” and “hardware.”
- Learn various file transportation methods.
- Learn features of the keyboard that make it different from a typewriter.
- Learn how your computer’s speed is measured and how to tell if your personal computer is fast enough to meet your needs (or a computer you may be considering purchasing)
First, let’s learn the basics about computers

versus

For computers, as for anything else, different styles exist. The different styles reflect different functions.
Types of Computers
From largest to smallest, the main types of standard computers are:
- desktop computer
- laptop computer/notebook
- personal digital assistant (PDA’s) and smart phones
Desktop Computers

- sit on your desk
- found in most businesses
- come with:
- a case, usually a tower, that holds the computers “parts”
- a monitor, also called a screen
- a mouse, used to move and select information on the monitor
- a keyboard, used to type in commands and documents
Laptop Computers

- designed to sit on your lap
- portable
- monitor and keyboard are built-in
- mouse built-in as a “touchpad”
- smaller models are referred to as “notebooks” or “netbooks”
Personal Digital Assistants (PDA’s)
- handheld devices
- function as “information managers”
- can connect to the Internet
- also called smart phones
 Apple iPhone is an example
Apple iPhone is an example
Now let’s consider the basic components of a computer.
Hardware
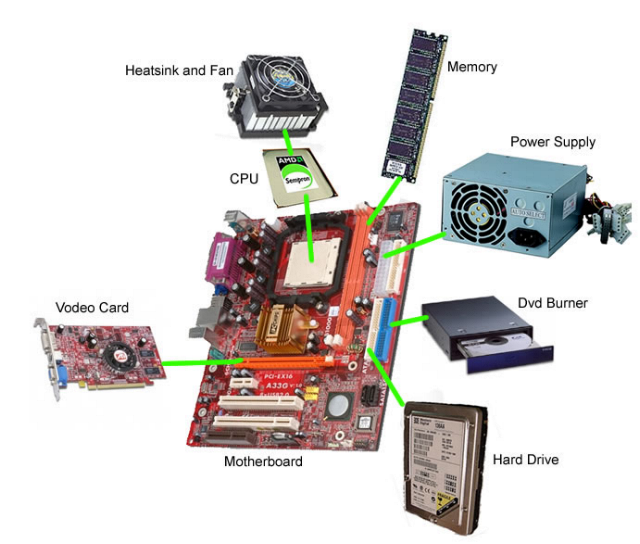
Hardware refers to computer’s physical components, which include:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Hard Drive
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Ports and Peripherals
Central Processing Unit (CPU)

The central processing unit (CPU) is the “brains” of a computer. It is often called a micro-processing chip. The CPU is a computation engine that:
- allows the computer to perform operations
- enables the computer to run software
- determines how fast the computer can make computations
- despite the disability, the CPU is a very small component.
Hard Drive
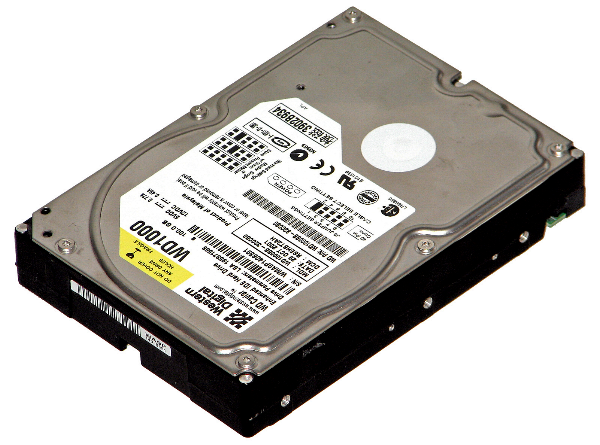

The hard drive stores your computers information and data. the hard drive:
- looks like an aluminum box
- contains electronic discs on which information is stored
- can be read and written to with arms that function like a very precise record player arm
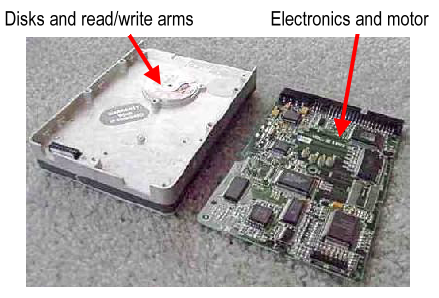

Three “hard disks” on the hard drive.

The read/write arm on the hard drive.
Random Access Memory (RAM)

- Random Access Memory (RAM) refers to a computer’s working memory.
- It affects how much information can be worked with at a given time.
- RAM affects how quickly a computer will start up and how fast it will let you work.
- .RAM is stored inside the computer on memory modules.
All of these pieces get wired together on a motherboard, hooked up to a power supply and a fan,and put inside a computer case, where they are held in place much like a car chassis holds the parts of a car in place.

Mother board
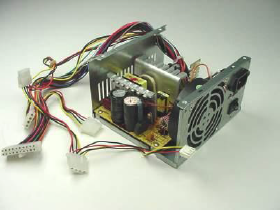
Power Supply

Assembled computer – inside a tower computer case

Car Chassis
Now let’s look at the final hardware component of a computer, the peripherals and ports.
- Peripherals are the external hardware devices they could plug into your computer.
- Laptops have fewer peripherals and their standard setup.
- Some examples of peripherals are printers and keyboards.

Printer

Keyboard
Ports on your Laptop
- Ports are docks, or connecting plugs, for your peripherals.
- They are the locations on your computer at which you connect peripherals.
- Each peripheral is designed to connect to a particular kind of port.
Ports on the left side of your laptop

USB plugs are common plugs used for digital cameras, modems, scanners, WebCams, etc. Look at your mouse’s plugged.

Different size USB plugs
Ports on the right side of your laptop

- The power cord plugs into a round port.
Now a brief look at the basic parts of the computer, let’s look at the systems that keep it running.

Software
Software is the entire set of programs and procedures associated with a computer.
Software comes in two forms:
- operating systems
- applications software
Operating Systems (OS)
- Operating System, or “OS,” software, is what lets the computer run.
- You can think of an OS as similar to the circulation system, since without an OS, a computer would be useless, just like our bodies would be useless without blood circulating.
- Operating systems very, but they all do the same thing – allow the computer to run.
- Microsoft Windows
- Mac
- Unix
- Linux
Application Software
- Also known as software applications, applications, or programs.
- Designed to help users perform particular tasks, such as word processing, spreadsheets, or creative computer painting.
- Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Paint are all examples of application software.
In comparison to operating software, application software might be considered comparable to a specific part of a body system, such as the eye, that allows us to perform a particular function, such as seeing.
Review of basic components of a computer
Hardware
- entral processing unit (CPU)
- hard drive
- random access memory (RAM)
- ports and peripherals
Software
- operating system (OS)
- application software