Module 6: Introduction to Popular AI Platforms
The explosion AI platforms and applications recently has changed the world. In this module, we explore some of the most popular platforms and uses across various industries.
- Goal: Equip learners with an understanding of popular AI platforms, their capabilities, and how they can be effectively utilized to drive innovation and solve real-world problems.
- Objective: Provide learners with a solid foundation in AI platforms, enabling them to understand their fundamentals, set up access, explore popular and specialty platforms, and recognize the importance of ethical considerations and responsible AI practices.
The module begins with an overview of AI platforms, explaining their connection to Large Language Models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Learners will then dive into the process of setting up access to AI platforms, including creating accounts, managing API keys, and configuring settings for optimal security and performance.
The module provides an in-depth look at popular AI platforms such as OpenAI ChatGPT, Anthropic Claude, and Google Gemini, highlighting their features, capabilities, and real-world use cases. Learners will also explore specialty AI platforms designed for specific industries and applications, showcasing the vast potential of AI to drive innovation and transformation across diverse domains.
Throughout the module, learners will gain practical guidance on leveraging AI platforms effectively, with hands-on tutorials and real-world examples. The module concludes by emphasizing the importance of ethical considerations and responsible AI practices, ensuring that learners are equipped to navigate the AI landscape with integrity and purpose.
- 6.1 AI Platforms: An Overview
- 6.2 Setting Up Access
- 6.3 Popular AI Platforms
- 6.4 Specialty AI Platforms
- 6.5 Summary
6.1 AI Platforms: An Overview
6.1.1 What are AI Platforms?
AI platforms are comprehensive software tools and environments that enable developers, businesses, and individuals to create, deploy, and manage AI applications and models. These platforms provide a range of pre-built components, libraries, and frameworks that simplify building AI solutions, making AI more accessible and efficient.
6.1.2 The Connection Between AI Platforms, Large Language Models (LLMs), and NLPs
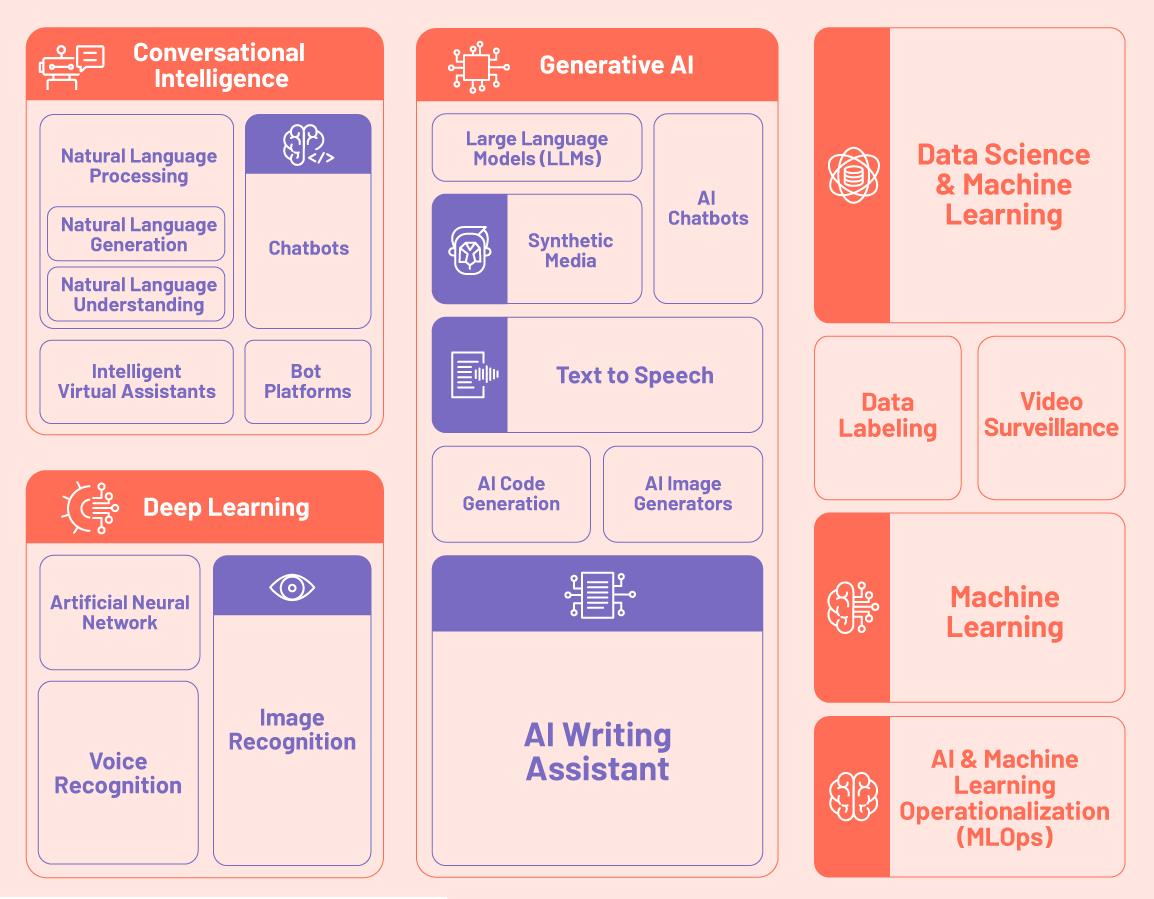
AI platforms often integrate with or leverage the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to power their advanced language understanding and generation features.
LLMs, such as GPT-3, BERT, and T5, are pre-trained on vast amounts of text data and can be fine-tuned or adapted for specific tasks within AI platforms.
NLP techniques, like tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition, are used to preprocess and analyze text data, enabling AI platforms to extract meaningful insights and generate human-like responses.
6.1.3 Capabilities and Potential of AI Platforms
![]()
AI platforms offer a wide range of capabilities, some common capabilities include:
- Writing: Generating, understanding, and manipulating text. This includes content creation, conversation, summarization, translation, and more.
- Video: Creating or modifying video content, including changing visual elements, adding effects, or generating new video clips from descriptions.
- Image: Generating and editing visual content based on textual descriptions or modifications to existing images.
- Code: Generate, identify and fix bugs, and optimize code for efficiency in numerous languages.
- Music Generation: Composing music or creating sound effects based on set parameters or styles, utilizing patterns in musical notation and theory.
- Speech Recognition: Converting spoken language into text, recognizing various voices and accents, and interpreting verbal commands.
- Speech Synthesis: Generating spoken language from text, mimicking various voices and languages, often used in virtual assistants and reading tools.
- Modeling: Design, model, and animate 3D characters and images.
- Data Analysis: Identifying patterns, predicting trends, sentiment analysis, content recommendations, and making decisions based on large datasets, applicable in marketing, finance, healthcare, etc.
The potential of AI platforms spans across industries, from healthcare and finance to marketing and entertainment, driving innovation and transforming business processes.
6.2 Setting Up Access
6.2.1 Creating Accounts and Navigating Dashboards
To get started with an AI platform, users typically need to create an account on the platform’s website or portal. This process usually involves providing basic information such as name, email address, and password. Once the account is set up, users can access the platform’s dashboard, which serves as the central hub for managing projects, resources, and settings.
6.2.1.1 Set up ChatGPT
Follow these steps to access OpenAI’s ChatGPT:
- Navigate to https://chatgpt.com/
- If you want to save your chat history, share chats, or personalize your experience, you will need to Sign up or Log in.
- Log in with this account
Note: The link provided will provide access to ChatGPT-3.5. Accessing ChatGPT-4 or any of the other features requires an account subscription.
6.2.2 API Keys and Developer Tokens
Many AI platforms require API keys or developer tokens to authenticate and authorize access to their services and functionalities. These credentials are unique to each user or application and must be kept secure. Users can generate and manage their API keys or tokens through the platform’s developer console or settings panel.
6.2.3 Initial Configuration Settings and Security Best Practices
Users should familiarize themselves with the available configuration options and security best practices for AI platforms before setting up an account. Implementing these measures is crucial for enhancing the safety, security, and responsible use of AI platforms while mitigating potential risks and vulnerabilities. Key security best practices include:
- Setting up two-factor authentication
- Configuring access controls and permissions
- Defining data privacy and retention policies
- Using content moderation APIs
- Constraining user input and limiting output tokens
By following these guidelines, users can ensure a more secure and reliable experience when working with AI platforms, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of the platform’s capabilities1.
[1] “Safety Best Practices” by OpenAI: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/safety-best-practices
6.2.4 Managing Costs and Understanding Billing Models
AI platforms often offer a range of pricing plans and billing models, such as pay-as-you-go, subscription-based, or tiered pricing based on usage or features. Users should carefully review and understand the costs associated with using the platform, including any additional charges for data storage, computation, or API calls. Setting up billing alerts, defining usage limits, and regularly monitoring usage can help users manage costs effectively.
[2] “Managing OpenAI API Costs: Strategies and Best Practices” by Mark Craddock: https://medium.com/@mcraddock/managing-openai-api-costs-strategies-and-best-practices-9b5d09eb2426
6.3 Popular AI Platforms
6.3.1 OpenAI ChatGPT
OpenAI is a leading AI research company that has developed state-of-the-art language models, including the widely-known ChatGPT. ChatGPT is a powerful conversational AI model that can understand and generate human-like text, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Models and Features
| Model | Description | Features |
| GPT-4 | An advanced set of models with improved reasoning capabilities and multimodal input support | Text, audio, and vision real-time reasoning – it accepts as input any combination of text, audio, image, and video and generates any combination of text, audio, and image outputs. |
| GPT-3 | A set of models that can understand and generate natural language or code | Text generation, code completion, question answering, summarization |
Uses and Capabilities
- Content creation and writing assistance: ChatGPT can help users generate high-quality content, such as articles, blog posts, and product descriptions, saving time and effort in the writing process.
- Code generation and debugging: The model can understand and generate code in various programming languages, assisting developers in writing and debugging code more efficiently.
- Question answering and research: ChatGPT can provide accurate and relevant answers to a wide range of questions, making it a valuable tool for research and information gathering.
- Summarization and text analysis: The model can quickly summarize long articles or documents, extracting key points and insights, which is useful for content curation and analysis.
- Creative writing and idea generation: ChatGPT can inspire users with creative ideas and prompts, helping them overcome writer’s block and generate unique content.
Resources
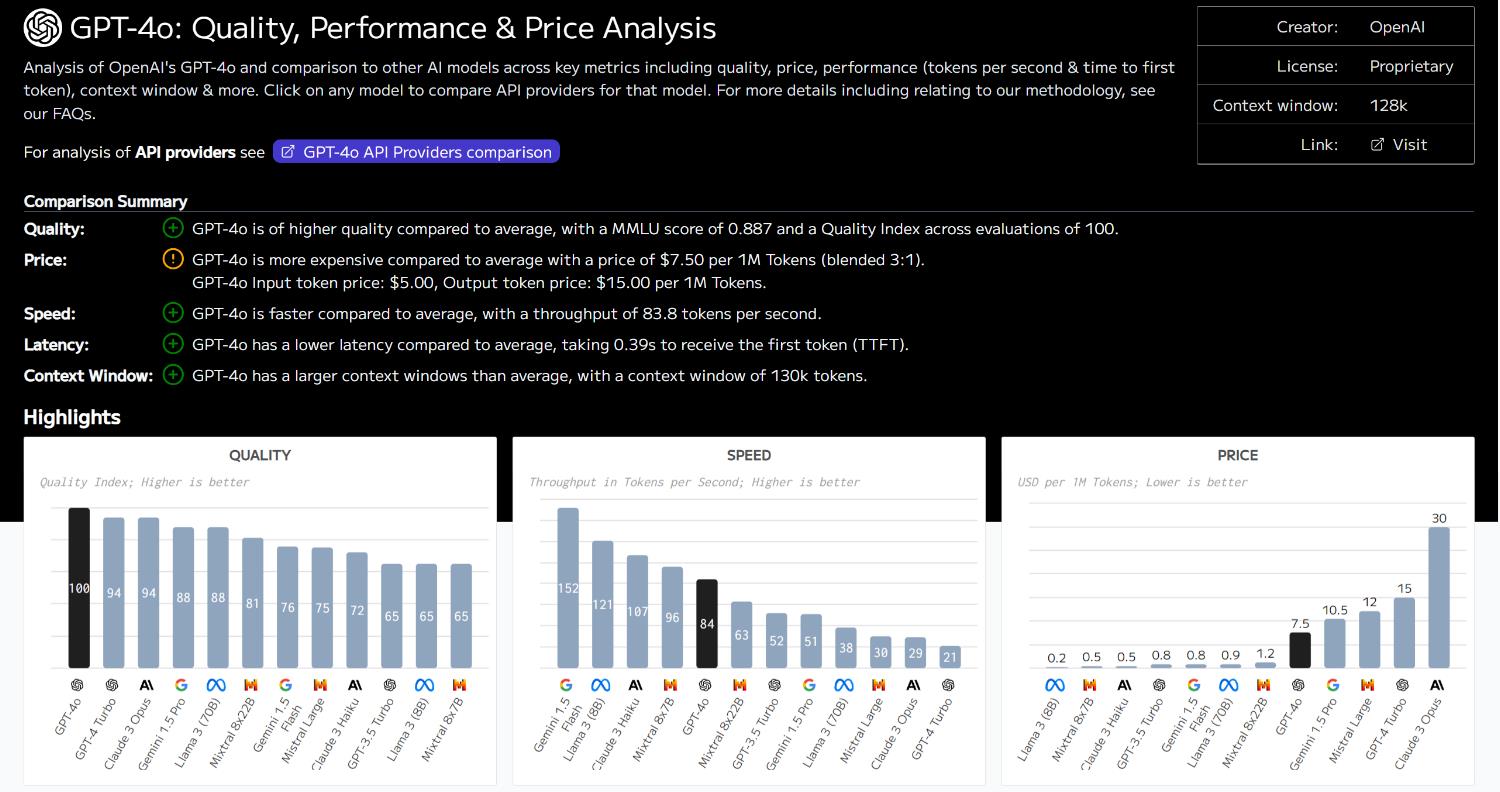
OpenAI GPT-4: Quality, Performance & Price Analysis
Analysis of OpenAI’s GPT-4 and comparison to other AI models across key metrics including quality, price, performance (tokens per second & time to first token), and context window.
6.3.2 Anthropic Claude
Anthropic is an AI research company that has developed Claude, a family of state-of-the-art large language models designed to provide high performance, safety, and steerability. Claude models excel at open-ended conversation, collaboration on ideas, coding tasks, and working with various types of data.
Models and Features
| Model | Description | Features |
| Claude 3 Opus | Most powerful model for highly complex tasks | Top-level performance, intelligence, fluency, and understanding |
| Claude 3 Sonnet | Ideal balance of intelligence and speed for enterprise workloads | Maximum utility at a lower price, dependable, balanced for scaled deployments |
| Claude 3 Haiku | Fastest and most compact model for near-instant responsiveness | Quick and accurate targeted performance |
Uses and Capabilities
- Open-ended conversation and collaboration: Claude models can engage in natural, context-aware conversations, making them ideal for customer support, virtual assistants, and collaborative tools.
- Text generation, editing, and summarization: These models can create, refine, and condense text content, streamlining content creation and management processes.
- Multilingual translation and understanding: Claude models offer improved fluency in non-English languages, enabling applications like translation services and global content creation.
- Vision and image processing: All Claude 3 models can process and analyze visual input, extracting insights from documents, processing web UI, and generating image catalog metadata.
- Enhanced steerability for controlled output: Claude models are designed to be easily steered, allowing developers to have more control over the model’s behavior and output quality.
Resources
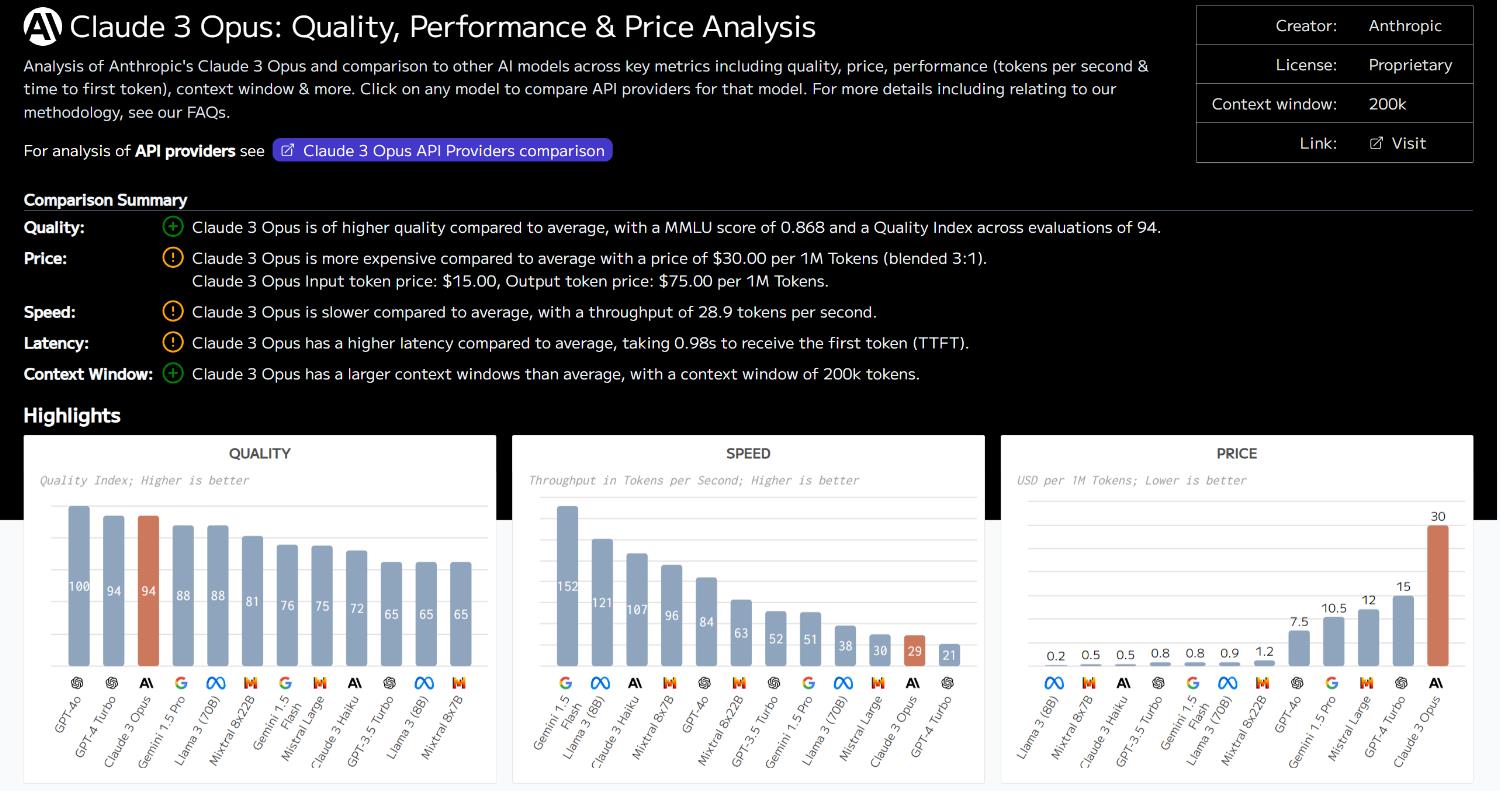
Claude 3 Opus: Quality, Performance & Price Analysis
Analysis of Anthropic’s Claude 3 Opus and comparison to other AI models across key metrics including quality, price, performance (tokens per second & time to first token), and context window.
6.3.3 Google Gemini
Google Gemini is a highly capable and general AI model developed by Google DeepMind. It is a multimodal model that can seamlessly understand, operate across, and combine different types of information, including text, code, audio, image, and video.
Models and Features
| Model | Description | Features |
| Gemini Ultra | Largest and most capable model for highly complex tasks | Sophisticated multimodal reasoning, state-of-the-art performance |
| Gemini Pro | Best model for scaling across a wide range of tasks | Advanced coding capabilities, reliable and scalable |
| Gemini Nano | The most efficient model for on-device tasks | Efficient performance, suitable for mobile devices and edge computing |
Uses and Capabilities
- Extracting insights from complex written and visual information: Gemini’s sophisticated multimodal reasoning capabilities can help make sense of large amounts of data, uncovering valuable knowledge and insights.
- Understanding and generating code in multiple programming languages: Gemini excels at coding tasks, understanding, explaining, and generating high-quality code in popular programming languages like Python, Java, C++, and Go.
- Advanced mathematical reasoning and problem-solving: The model demonstrates strong performance in solving complex mathematical problems and explaining its reasoning, making it valuable for educational and scientific applications.
- Multimodal understanding and reasoning across text, images, audio, and video: Gemini’s native multimodality allows it to effectively process and analyze various types of input simultaneously, enabling more comprehensive and nuanced understanding.
- Integration with Google products and services for enhanced user experiences: Gemini is being integrated into various Google products, such as Gemini (Bard), Pixel devices, and Google Search, to provide users with more advanced and efficient AI-powered features.
Resources
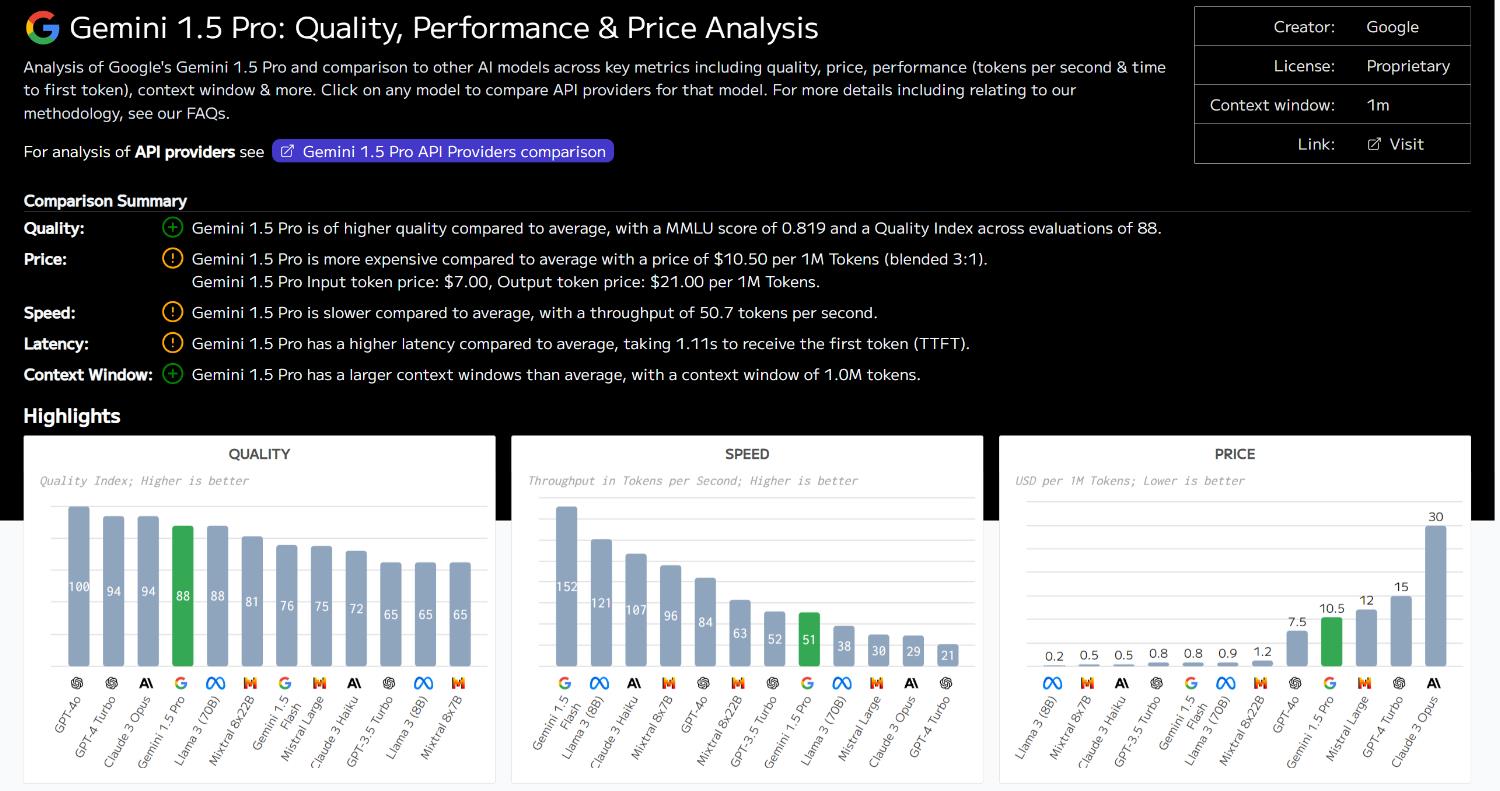
Gemini 1.5 Pro: Quality, Performance & Price Analysis
Analysis of Google’s Gemini 1.5 Pro and comparison to other AI models across key metrics including quality, price, performance (tokens per second & time to first token), and context window.
6.3.4 Comparison: ChatGPT, Claude, & Gemini
| Aspect | OpenAI | Anthropic Claude | Google Gemini |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company | OpenAI | Anthropic | Google DeepMind |
| Key Models | GPT-3.5, GPT-4o | Claude 3 | Gemini 1.5 |
| Model Sizes/Variants | – | Opus, Sonnet, Haiku | Ultra, Pro, Nano |
| Multimodal Capabilities | Text, Audio, Image, Video (GPT-4o) | Text, Code, Images, Audio | Text, Code, Audio, Image, Video |
| Key Features | Advanced reasoning capabilities | High performance, safety, and steerability | Sophisticated multimodal reasoning |
| Full multimodal input support (GPT-4o) | Multilingual fluency | Advanced coding capabilities | |
| Strong language understanding, generation, and reasoning | Enhanced vision and image processing | State-of-the-art performance | |
| Improved model steerability | Efficient on-device performance (Gemini Nano) | ||
| Notable Use Cases | Content creation and writing assistance | Open-ended conversation and collaboration | Extracting insights from complex data |
| Code generation and debugging | Text generation, editing, and summarization | Understanding and generating code | |
| Question answering and research | Multilingual translation and understanding | Advanced mathematical reasoning | |
| Summarization and text analysis | Vision and image processing | Multimodal understanding and reasoning | |
| Creative writing and idea generation | Controlled output through enhanced steerability | Integration with Google products and services | |
| Availability and Integration | Available through OpenAI API | Available through Anthropic’s API, AWS Bedrock, and GCP Vertex AI | Integration with Google products (Bard, Pixel devices, Google Search) |
Comparison between models, their sizes or variants, multimodal capabilities, key features, notable use cases, and availability or integration options.
6.4 Specialty AI Platforms
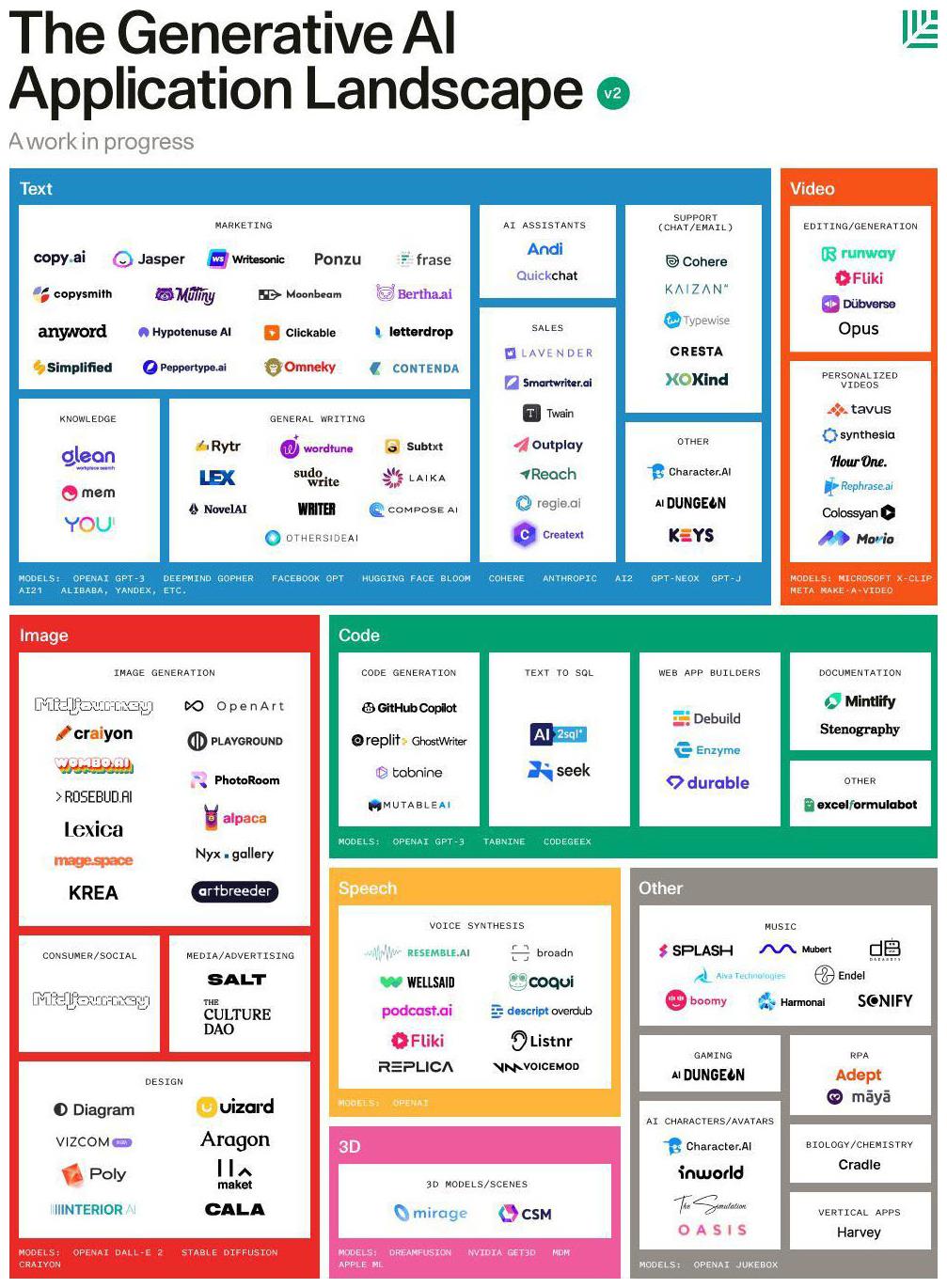
Since the release of OpenAI to the public, the AI tool marketplace has rapidly grown, with thousands of specialty tools designed to cater to specific functions and industries. These tools are built on a variety of foundations, each offering unique benefits and capabilities.
Some tools, like Leonardo.ai, are built on fine-tuned models (Stable Diffusion), leveraging the power of established AI technologies to provide targeted solutions. Others, like Jasper.ai, are focus-trained (marketing content) on specific tasks or domains to deliver highly optimized results. Using these specialized tools can often lead to increased productivity and efficiency compared to more general-purpose AI platforms.
To help you navigate this vast landscape, I’ve categorized some of the most popular AI tools based on their primary function or purpose. Below, you’ll find a list of categories along with a few top tools in each group.
Text
- Copywriting: Jasper.ai, Copy.ai, Writesonic
- Email Assistant: Superhuman, Mailman, Front
- General Writing: Grammarly, Hemingway, ProWritingAid
- Paraphrasing: Quillbot, Spinbot, Paraphrasing Tool
- Prompts: Promptist, PromptBase, Midjourney Prompt Tool
- SEO: Surfer SEO, MarketMuse, Frase
- Social Media Assistant: Sprout Social, Hootsuite, Buffer
- Storyteller: ShortlyAI, Sudowrite, Subtxt
- Summarizer: SMMRY, Resoomer, Scribber Text Summarizer
Image
- Art: DALL-E, Midjourney, Leonardo.ai
- Avatars: Lensa, Ready Player Me, Genies
- Design Assistant: Uizard, Khroma, Visily
- Image Editing: Luminar AI, Pixlr, Canva
- Logo Generator: Looka, BrandMark, Hatchful (by Shopify)
- Image Generator: Craiyon, Artbreeder, StarryAI
Code
- Code Assistant: GitHub Copilot, Codota, Kite
- Developer Tools: OpenAI Codex, Tabnine, Mutable
- Low Code/No Code: Bubble, Webflow, Adalo
- Spreadsheets: Grid, Airtable, Coda
- SQL: SQLFlowGrid, MindsDB, Text2SQL
Audio
- Editing: Descript, Cleanvoice, Veed Audio Editor
- Music: Boomy, Jukebox, AIVA
- Text To Speech: NaturalReader, Resemble, Speechelo
- Transcriber: Otter.ai, Trint, Sonix
Video
- Personalized Videos: Synthesia, Rephrase.ai, Hour One
- Video Editing: Flixier, Kamua, Vidyo
- Video Generator: Lumen5, InVideo, Waymark
Business
- Customer Support: Intercom, Zendesk, Freshdesk
- E-commerce: Dialogue/a>, ManyChat, Octane AI
- Education Assistant: Duolingo, Quizlet, Eduaide.AI
- Finance: Wallet AI, Cleo, Olivia
- Human Resources: Eightfold.ai, Textio, Ideal
- Legal Assistant: DoNotPay, Legartis, LawGeexProductivity: Notion, ClickUp, Asana
- Sales: Gong, Chorus.ai, Outreach
- Startup: Pitchdeck, Finta, Looka
Other
- Fun: AI Dungeon. Botify, Replika
- Gaming: Promethean AI, Modl.ai, Art Imposter
- Health care: Ada Health, Babylon, K Health
- Life Assistant: X.ai, Julie Desk, Ohai.ai
- Research: Iris.ai, Elicit, Dimensions
- Search Engine: Neeva, You.com, Perplexity
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, new tools are constantly emerging to address a growing range of use cases and industries. To stay updated on the latest developments, consider exploring the following AI tool aggregator websites:

Additional resources:
- Futurepedia (https://www.futurepedia.io/): A comprehensive directory of AI tools, categorized by function and industry, with detailed descriptions and user reviews.
- Future Tools (https://www.futuretools.io/): A curated collection of AI tools, featuring the latest and most innovative solutions across various categories.
- Find My AI Tool (https://findmyaitool.com/): A search engine specifically designed to help users discover AI tools based on their needs and preferences.
- There’s An AI For That (https://theresanaiforthat.com/): An easy-to-navigate website showcasing a wide range of AI tools, organized by use case and functionality.
- Easy With AI (https://easywithai.com/): A user-friendly platform that helps beginners and professionals alike find the right AI tools for their projects and goals.
These websites are regularly updated with new tools and categories, making them valuable resources for anyone looking to stay at the forefront of the AI tool landscape. By leveraging these resources and exploring the various categories of AI tools available, you can unlock new possibilities and streamline your workflows in ways that were previously unimaginable.
6.5 Summary
This module provided an in-depth look at popular AI platforms, covering their key features, setup processes, and practical applications. By gaining a solid understanding of these platforms, learners can make well-informed choices about which tools are best suited to their specific needs and objectives.
The module has explored the interplay between AI platforms, Large Language Models (LLMs), and Natural Language Processing (NLP), showing how these technologies combine to power a wide range of applications across different sectors. It has also provided detailed guidance on setting up accounts, handling API keys, and configuring settings to ensure security and optimal performance.
The module has also shed light on specialty AI platforms, which are designed to cater to specific industries and use cases. These platforms showcase the enormous potential of AI to drive innovation and transformation across a diverse range of domains, from creative industries to healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
As learners explore the AI landscape, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations and responsible AI practices. By ensuring that these technologies are used in ways that align with societal values, promote transparency, and maintain accountability, we can work towards a future in which AI benefits everyone.