What is Search Engine Optimization?
Search Engine Optimization or SEO is the process of improving the visibility of a website or a web page in the search engine “natural,” or unpaid (“organic” or “algorithmic”) search results.
All major search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo have such results, where web pages and other content such as videos or local listings are shown and ranked based on what the search engine considers most relevant to users.
Payment isn’t involved, as it is with paid search ads.
The key to ranking web pages is to understand how these search engines work. By learning the Who, What, Where, How, and Why’s of search engines operation and data collection, you will have a better chance for high rankings…
Ask yourself a few simple (yet amazingly complex) questions:
- How did Google discover my web page?
- What does it do when visiting my web page?
- Where did it go when it left my web page?
- Did Google stay on my website or go somewhere else?
 How a Search Engine Works
How a Search Engine Works
Search engines have two major functions:
- Crawling & building an index.
- Providing answers by calculating relevancy & serving results.
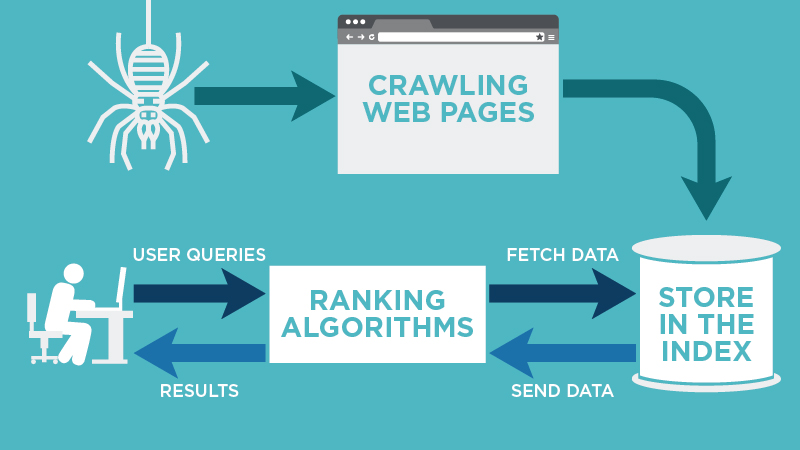
1. Crawling & Building an Index

Imagine the World Wide Web as a network of stops in a big city subway system…
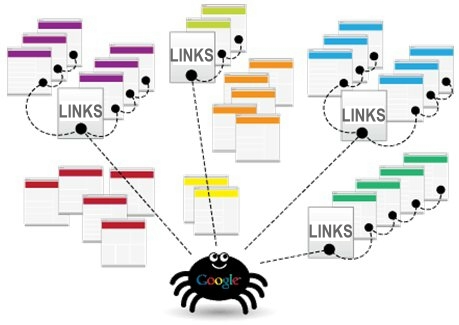
Each stop is its own unique document (usually a web page, but sometimes a PDF, JPG, a video, or other file). The search engines need a way to “crawl” the entire city (the Internet) and find all the stops (web pages) along the way, so they use the best path available – links.
Through those links, search engines’ automated robots, called “search bots,” “web crawlers,” or “spiders” can reach the billions of interconnected documents online.
Once the engines find these pages, they next decipher the code from them and store selected pieces in massive hard drives, to be recalled later for a search query. All of this collected data (billions of of web pages) can be accessed in fractions of a second.
 To accomplish the monumental task of holding billions of pages that can be accessed in a fraction of a second, the major search providers (like Google, Bing, and Archive.org) have constructed data centers all over the world.
To accomplish the monumental task of holding billions of pages that can be accessed in a fraction of a second, the major search providers (like Google, Bing, and Archive.org) have constructed data centers all over the world.
These monstrous storage facilities hold thousands of computers processing large quantities of information. After all, when a person performs a search at any of the major engines, they demand results instantaneously – even a 1 or 2 second delay can cause dissatisfaction, so the engines work hard to provide answers as fast as possible.
2. Providing Answers by Calculating Relevancy & Serving Results
Search engines are answer machines. When a person looks for something online, it requires the search engines to scour their billions of documents and do two things – first, return only those results that are relevant or useful to the searcher’s query, and second, rank those results in order of importance by perceived usefulness.
![]() Search Engine Optimization is about influencing “relevance” and “importance” of web pages.
Search Engine Optimization is about influencing “relevance” and “importance” of web pages.
To a search engine, relevance means more than simply finding a page with the right words on it. In the early days of the web this was a simple task – there were only a few million web pages – and they didn’t go much further than find the first page in their data.
How many web pages are there today? Nobody really knows for sure, but the indexed web contains at least 4.45 billion pages. To give you an idea of the growth of the internet, Google had indexed 30 trillion pages back in March 2013.
Through evolution and growth, search engines have made significant strides in presenting better results to searchers. There are 100’s of factors influencing web page relevance, many of which we’ll discuss throughout this course.
How Do Search Engines Determine Search Result Ranking?

Currently, one of the major factors used by the major engines is popularity – the more popular a site, page or document is, the more valuable the information.
![]()
Popularity and relevance aren’t determined manually.
Search engines employ complex mathematical equations (know as algorithms) to sort though all of the collected data and then determine what is important and relevant to a specific search query AND in what order to display the search results. In SEO, we often refer to this as “ranking factors.”
What Are the Ranking Factors?
Great question. The complicated algorithm formulas (used by Google) are more closely guarded than most military secrets.
Here’s a basic outline direct from Google and Bing on optimization and best practices…

Google recommends the following to get better rankings in their search engine:
- Make pages primarily for users, not for search engines.
- Don’t deceive your users or present different content to search engines than you display to users (commonly referred to as cloaking).
- Make a site with a clear hierarchy and text links. Every page should be reachable from at least one static text link.
- Create a useful, information-rich site, and write pages that clearly and accurately describe your content.
- Make sure that your <title> elements and ALT attributes are descriptive and accurate.
- Use keywords to create descriptive, human friendly URLs. Provide one version of a URL to reach a document, using 301 redirects or the rel=”canonical” element to address duplicate content.

Microsoft recommends the following to get better rankings in their search engine:
- Ensure a clean, keyword rich URL structure is in place.
- Make sure content is not buried inside rich media (Adobe Flash Player, JavaScript, Ajax) and verify that rich media doesn’t hide links from crawlers.
- Create keyword-rich content based on research to match what users are searching for.
- Produce fresh content regularly.
- Don’t put the text that you want indexed inside images. For example, if you want your company name or address to be indexed, make sure it is not displayed inside a company logo.
I Know What You’re Thinking – There has To Be MORE!
Since the beginning of web search (around 1994), search marketers have shared and found information about how the search engines rank pages and how to achieve better positioning.
Like a detective, you have to search through the clues…
Search engines are constantly updating their algorithms – what worked yesterday might not work tomorrow. If you want to remain successful with SEO, it requires constant research, reading, and testing to stay current.
![]() READING: For a more in-depth discussion on Internet search engines, how they build an index of data and what Boolean operators are, check out this article by HowStuffWorks.com: How Search Engines Work.
READING: For a more in-depth discussion on Internet search engines, how they build an index of data and what Boolean operators are, check out this article by HowStuffWorks.com: How Search Engines Work.
![]() READING: Google has produced a great explanation of “how” they work. From crawling and indexing websites to search result algorithms and fighting website spam. I highly recommend you read through this illustrated tutorial: How Search Works.
READING: Google has produced a great explanation of “how” they work. From crawling and indexing websites to search result algorithms and fighting website spam. I highly recommend you read through this illustrated tutorial: How Search Works.
![]() READING: It’s amazing what you can find when using Google! Here’s the patent from Lawrence Page (1/2 of Google) and his Method for node ranking in a linked database.
READING: It’s amazing what you can find when using Google! Here’s the patent from Lawrence Page (1/2 of Google) and his Method for node ranking in a linked database.
It’s time for an experiment![]() ! Experiment with your own domains and see what works. Use the search engines to test theories and form opinions based on your results. This might seem like overkill to you, but the knowledge gained through testing becomes invaluable.
! Experiment with your own domains and see what works. Use the search engines to test theories and form opinions based on your results. This might seem like overkill to you, but the knowledge gained through testing becomes invaluable.